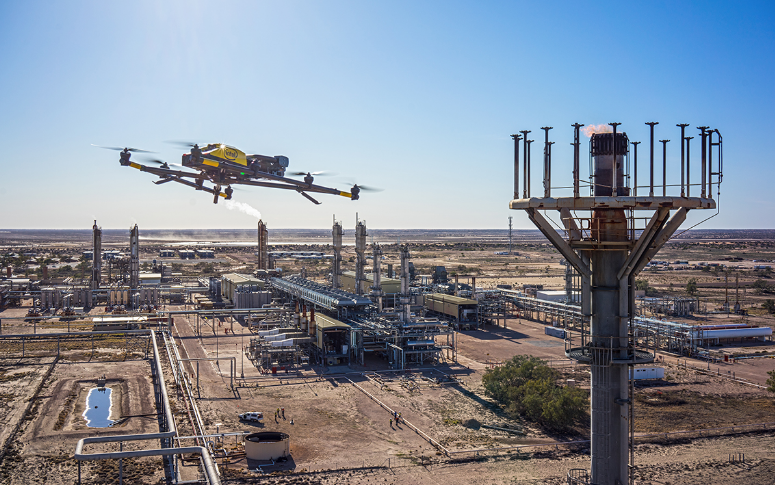
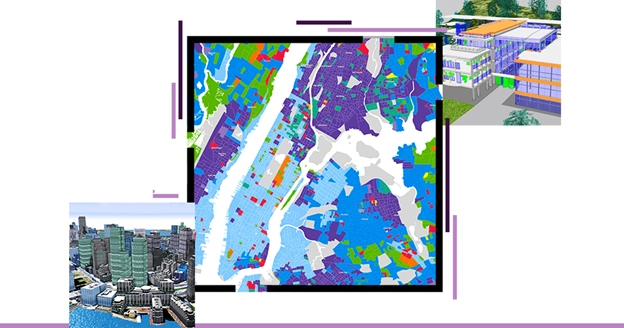
Ever wondered how Google Maps knows the exact layout of your city? Engineers use geospatial surveying to conduct accurate planning of extensive infrastructure development projects. Geospatial surveying exists as a forceful technology that produces detailed representations of the physical world.
Modern mapping relies on geospatial surveying to construct structures while urban planners and disaster managers use it for their operational needs. Without it, we’d be lost literally. Spatial data produced through geospatial surveying enables authorities together with organizations and research institutions to conduct accurate evidence-based decision-making.
The use of geospatial surveying allows businesses across industries to create more accurate processes and resulting projects through detailed spatial data collection. The technology utilizes modern equipment which includes GPS, LiDAR, and drones to produce accurate 3D surface maps and models of the Earth. This guide presents concepts in a basic approach to explain the value and usage of this technology.
What is Geospatial Surveying?
Geospatial surveying constitutes the scientific process of data collection and processing alongside data interpretation that focuses on Earth’s surface features. Geospatial surveying utilizes GPS, LiDAR, remote sensing, Geographic Information Systems (GIS,) and advanced technologies to generate detailed landscapes, building details, and infrastructure 3D models and accurate maps.
Geospatial surveying accepts extensive amounts of spatial data from different sources while traditional land surveying remains limited to measuring borders and altitudes. The ability to construct detailed dynamic maps through this method enables surveyors to apply their creations in industries such as construction as well as agriculture urban planning, disaster response and environmental monitoring.
Providing real-time data is one of the main benefits of geospatial surveying. Experts can observe environmental trends, keep an eye on landscape changes, and assess significant regional alterations with unmatched accuracy by utilizing drones and satellite imagery. Because of these capabilities, geospatial surveying is a vital tool for global governments, corporations, and academic institutions.
How it Works?
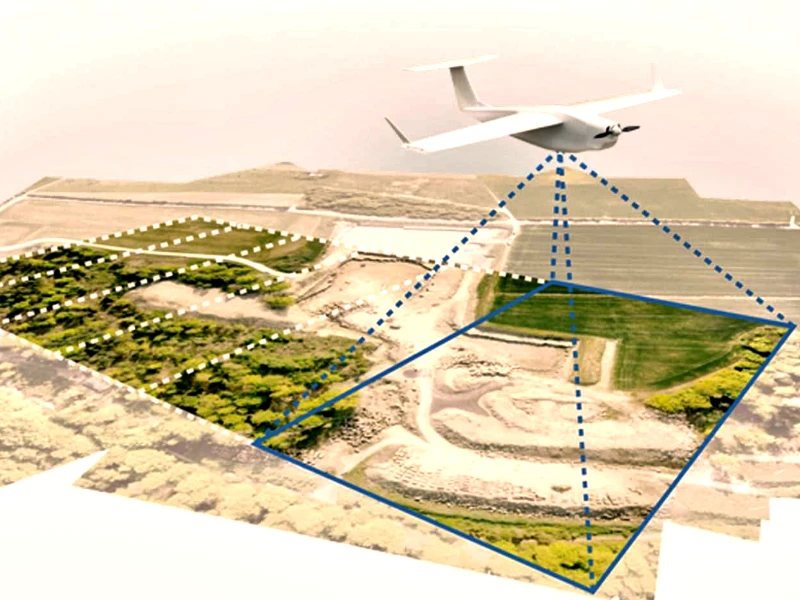
1. Gathering information
Getting geographic data straight from the source is the initial stage in the geospatial surveying process. Survey teams use satellites, drones, and aerial images, together with GPS receivers and a variety of ground-based sensors. Together with topographical details and mapping of the land’s use, the recorded data contains a wealth of information regarding surface factors including land height.
A common instrument used by contemporary geospatial surveyors is LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), which creates accurate three-dimensional terrain maps and structure representations using laser pulses. By tracking urbanization, coastal erosion, and deforestation, remotely obtained technology is a vital tool for tracking changes in our environment.
2. Processing & Analysis
The collected raw data is processed using complex computational algorithms and Geographic Information algorithms (GIS) software platforms. In order to convert data into usable digital elevation models and 3D visualizations, users must first clean datasets before linkages between spatial models are built.
Professionals can use GIS platforms to stack various data layers and compare historical and current maps to create analytics that help with planning decisions. Combining machine learning techniques with artificial intelligence (AI) enhances predictive modeling and automated data processing.
3. Application & Decision Making
Geospatial surveying concludes with the implementation of processed information for actual problem solutions. Designers rely on GIS technology when building infrastructure projects along with urban developers who optimize transportation infrastructure and city planning. Coronavirus reactive teams implement digital geographic mapping to evaluate flood risk zones and wildfire locations in order to improve their coordinated relief response efforts.
The agricultural applications of geospatial surveying enable farmers to inspect their soil vitality while observing plant growth and implementing better irrigation techniques. Business operations make use of geospatial information to study consumer market shifts as well as redesign their delivery routes and service territories through location-based IT applications.
Geospatial surveying benefits from cloud computing technology and real-time data streaming so it is gaining wider utilization throughout multiple industries. Geospatial data visualization and interpretation transformed decision-making into a powerful capability that organizations use for efficiency and sustainability improvements
Essential Tools for Geospatial Surveying
Today, surveying operations rely on cutting-edge technical tools. Surveying requires a number of fundamental tools, some of which are listed below:
1. The GPS
(Global Positioning System) GPS satellites allow surveyors to pinpoint precise geographic locations throughout the world. Because it provides centimetre-level accuracy, RTK GPS is crucial for construction and navigation.
The GPS technology serves essential functions in surveying applications to guide navigation systems develop infrastructure plans and structure land parcel information. The use of GPS technology in large-scale projects assures minimal mistakes while decreasing expenses and delivering accurate data.
Read information about GPS precision from U.S. Government GPS.gov.
2. Light Detection and Ranging, or LiDAR
The distance-measurement capacity of LiDAR depends on its lasers which transmit precise pulses. The technology finds its extensive applications in mapping the landscape together with flood modelling and forestry work.
The use of LiDAR technology produces detailed three-dimensional building and vegetation and topographical maps through laser beam transmission recordings. The combination of geological study with infrastructure advancement and environmental assessment makes it necessary for numerous purposes.
Learn more about LiDAR: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA)
3. Drones & UAVs (Unmanned Aerial Vehicles)
UAVs use their ability to fly to areas other machines cannot access to generate detailed aerial records of terrain areas. Proficiency along with cost efficiency improvements throughout surveying operations bring new standard changes to land survey practices.
Survey-grade drones that use LiDAR sensors together with high-resolution cameras enable the production of precise maps that support urban development projects as well as the monitoring of agricultural fields and construction sites. Surveyors can use drone versatility to collect both swift and accurate wide-area data through their diverse mapping capabilities.
The Federal Aviation Administration provides an explanation of drone mapping operations.
The Importance of Geospatial Surveying
Why is geospatial surveying vital? Here are some of the main points:
● Lies within unmatched accuracy: The measurement of large projects such as construction and land development gets more precise with fewer mistakes due to advanced technology like GPS, LiDAR, and remote sensing.
● More cost-effective: Increase the speed and efficiency of the surveying process, assisting businesses in conserving time and resources by minimizing manual labor.
● Supports enhanced decision making: Providing urban planners along with engineers and policymakers further with detailed insights from GIS and spatial analytics enables infrastructure and land use to be optimized.
● Aids in Environmental Protection: Helps to support conservation efforts, keep track of climate change, monitor deforestation, and assist in disaster preparedness by evaluating flood, earthquake, and hurricane-prone areas.
● Scalability: Adapts to various industries, whether it be for a large smart city project or a small land survey, geospatial surveying allows flexibility.
● Aids in improved safety globally: By accurately outlining hazardous zones along with assessing infrastructure conditions, geospatial data assists in increasing workplace safety while reducing the chances of accidents.
● Smart urban development: Geospatial information helps design smart cities through housing and zoning regulations, public transportation, and other utilities.
Geospatial Surveying: Some Interesting Facts
● LiDAR technology was able to map the Great Wall of China! Historians and archaeologists have benefited from LiDAR technology as it was able to uncover walls and structures previously hidden under vegetation.
● Geospatial surveying is used for mapping Mars, and NASA does just that! The Curiosity rover uses tools such as LiDAR to move about the Martian surface. This enables scientists to study the geology of planets and to prepare for future explorations.
● In 2021, drones were used to survey the regions of the world’s largest ship cemetery. Many undiscovered shipwrecks within Scotland’s Rosyth dockyard were unveiled using UAV technology.
● Google has taken this phenomenon further through Google Earth, which is based on geospatial surveying. Now, everyday users and businesses alike can easily navigate different regions with the help of satellite imagery and GIS data.
● In Central America, LiDAR has helped uncover forgotten towns of the Mayans underneath the heavy jungle. Such sophisticated uses of technology have completely transformed archaeology.
● Geospatial technology has received praise from wildlife protection agencies that track illegal deforestation and poaching, monitoring animal movements on the ground from satellites.
The application of geospatial technology for efficient tracking and management of disasters such as hurricanes or earthquakes is limitless.
Some Case Studies of Geospatial Surveying
1. Nepal Earthquake 2015: Disaster Response
Analysis and distribution of relief assistance after the 2015 Nepal quake became possible through geospatial surveying techniques. Police employed satellite images and remote sensing systems to quickly find both collapsed structures and impaired facilities. Emergency responders could make proper gains with their rescue efforts by using this system to direct their resources properly.
Operating through GIS platforms made it possible to map disaster regions precisely so humanitarian groups could track through hard-to-navigate terrain to deliver aid to distant communities. Geospatial technology allowed emergency crews to act faster during disasters thus they saved multiple lives while achieving better coordination throughout relief operations.
2. Smart Cities in Singapore
As a global frontrunner in smart city development, Singapore utilizes geospatial tools including GIS alongside LiDAR for managing infrastructure and making urban plans. The government leverages 3D mapping combined with real-time geospatial data to supervise traffic patterns optimize public transportation systems and achieve sustainable environmental goals.
Geospatial data enables the Land Transport Authority of Singapore to forecast traffic jams so they can optimize their road system operations. The process of using LiDAR-based mapping has proven essential for developing new urban areas while achieving maximum protection for natural resources.
The sustainable urban planning of geospatial surveying in Singapore functions as a blueprint for global cities to build up their own geospatial surveying plans.
3. Amazon Rainforest Deforestation Monitoring
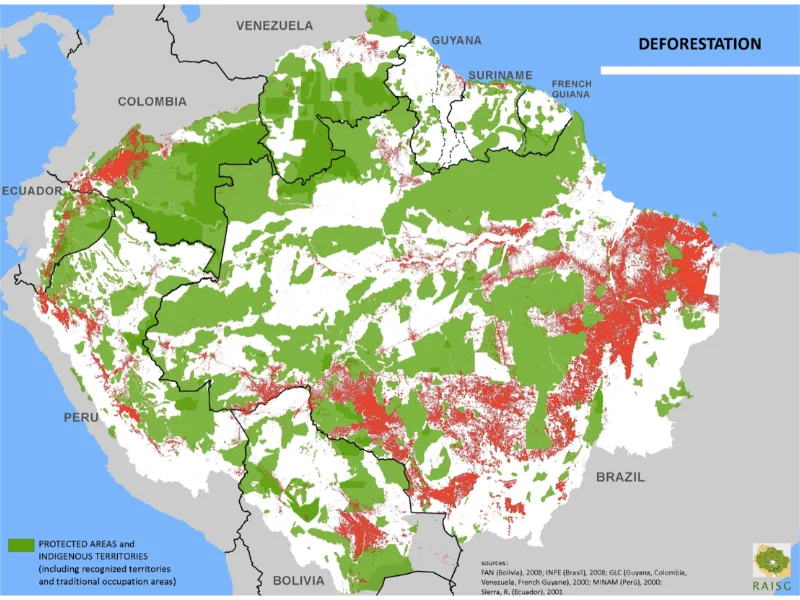
Rapid deforestation affects the Amazon rainforest which people call the Earth’s “lungs.” Conservation teams need geospatial survey methods to determine deforestation progress while fighting illegal forest destructors.
Real-time updates of forest cover modifications become possible through a combination of remote sensing technology that features satellite imagery and LiDAR. The software analyses changes in the area and selects vulnerable locations for identification. Environmental policy enforcement and biodiversity protection rely on this data which conservation groups together with government agencies utilize.
The Global Forest Watch stands out as a notable project because it tracks deforestation patterns by using geospatial data for sustainable land management promotion. Ongoing geospatial monitoring systems enable authors to enhance their deforestation control and climate change combat operations.
The Advantages of Geospatial Surveying
Geospatial surveying is not solely the domain of cartographers. It is an important aspect of different sectors, improving productivity, accuracy, and choices in all sectors.
1. Urban Development and Public Infrastructure Services
Every urban area harnesses the potential of geospatial data for precise urban development. It aids city planners in formulating the design of roads, bridges, public transport, and even setting up smart cities. The GIS technology offers real-time information on land use, traffic, the existing transport infrastructure, population density, and other socio-economic indicators for better planning and balanced allocation of resources.
Due to geospatial data, the areas suffering from overpopulation can be prevented, thereby assuring the public half congested cities safer cities, and smoother environments. The combination of GIS technology in urban planning ensures more sustainable, efficient, and resilient cities.
2. Construction and Civil Engineering Works
In construction and civil engineering schemes, geospatial surveying is crucial. In the construction of skyscrapers, tunnels, bridges, and roads, the construction surveyors assist with the fixed measurements.
By the use of GPS and LiDAR technologies, engineers will be able to map out prospective sites, and soil conditions at different depths, and even determine the building strengths. This increases the accuracy of estimates, ensures greater safety, and speeds up project timelines.
In addition, the conversion of data to a three-dimensional model helps architects and designers of geospatial data.
3. Agriculture & Land Management
Agronomists together with farmers who implement geospatial technology optimize their production of crops as well as water resources management and land practices. Electronic systems based on GIS and remote sensing help farmers check soil water content as well as find plant diseases and evaluate plant health status.
Farmers can achieve better production numbers while spending less on operations and practicing sustainable agriculture because they combine location-based data for their decisions.
Geospatial surveying enables authorities along with agricultural organizations to develop superior land use policies by assisting with soil conservation and land classification activities.
Learn: What is GIS in agriculture?
4. Disaster Management & Climate Change
Geospatial surveying functions as a fundamental process to reduce the negative outcomes of natural disasters alongside climate change effects. Governing bodies and aid organizations deploy satellite imagery and Geographic Information System mapping to forecast observe and handle disasters including hurricanes, floods, earthquakes, and wildfires.
Emergency responders can identify hazardous locations build effective evacuation plans and distribute resources due to geospatial information collected during a crisis. Analysing past disaster information enables authorities to develop emergency readiness plans that reduce both casualty numbers and property destruction.
Geospatial surveying serves climate change studies by helping scientists observe the changes in deforestation patterns as well as glacier degeneration and increasing sea levels alongside shifting patterns of weather. The acquired insights have important roles in worldwide climate change battles and environmental defence strategies.
5. Mining & Resource Management
Organizations within the mining industry require extensive use of geospatial surveying to identify mineral deposits as well as verify excavation advancement steps and regulatory standards. Their combination of GIS and remote sensing technologies enhances the accurate tracing of underground geological deposits, resulting in lower environmental damage.
Engaging in the mapping of mineral deposits together with geological formation analysis enables mining engineers to achieve efficient operations without creating excessive waste. The evaluation of environmental conditions relies on geospatial surveying for the purpose of validating mining compliance with safety and sustainability standards.
Water resource management receives major benefits from the applications of geospatial technology. Public authorities and conservation groups leverage GIS technology to track water resources alongside ecosystem health and toxic substances levels which enables them to create more effective decisions for preserving water sustainability.
Do you know GIS services in the mining sector?
6. Transportation & Logistics
Geospatial surveying is essential to the transportation industry for traffic control, fleet management, and route optimization. Logistics firms can watch vehicle movements, develop more effective delivery routes, and use less fuel with the aid of GIS technology.
Geospatial surveying in aviation and maritime services enables correct navigation thus cutting down danger and enhancing safety operations. The new era of transportation will come into view thanks to self-driving cars which use high-definition geospatial mapping to guide themselves along the streets independently.
You might be intrested in application of gis in transportation.
The Future of Geospatial Surveying
The future is exciting! The upcoming technologies AI, 5G, and real-time 3D mapping systems will elevate geospatial surveying to unprecedented heights. Here’s what’s coming:
AI combined with Machine Learning technology will help expedite analysis procedures in order to enhance decision-making speed. Autonomous Surveying Drones operate with minimal human supervision for survey work. Faster data analysis systems enable real-time disaster and urban growth observations.
The number of job opportunities for geospatial professionals is increasing rapidly in the market. Having an interest in both high-tech approaches and making a significant difference will help you thrive in this field.
Conclusion
The modern world exists in ways we commonly overlook because of geospatial surveying. Geospatial surveying elevates development planning across urban areas while delivering important benefits for disaster response management. Geospatial survey data serves governments, businesses, and research teams for decision-making improvement, resource optimization, and technological progress.
Geospatial surveying provisions cities with better functionality through optimized transportation designs and utility services and zoning control systems. Engineers need geospatial data for accurate infrastructure work because it stops wasteful mistakes while boosting project safety.
Geospatial technology enables new developments in artificial intelligence and autonomous vehicles alongside intelligent city framework initiatives. Geospatial surveying will advance the creation of our future which will result from the ongoing development of cloud computing, real-time data processing, and machine learning frameworks.