Most people use Geographic Information Systems (GIS) every day without realising it. Whether you check traffic on your phone, track a parcel, or look up the nearest restaurant, GIS is quietly working behind the scenes. It connects data to location, showing where things happen, how they relate, and why it matters.
Once used mainly by scientists and governments, GIS now shapes how cities grow, how services run, and how people move through their daily lives. It makes complex systems work smoothly, saving time, money, and effort for both individuals and organisations.
Here’s a closer look at how GIS fits into everyday life, from the phone in your hand to the cities we live in.
1. Navigation and Traffic Updates
When you open Google Maps or Waze to find the fastest route, GIS makes it happen. These apps analyse real-time data from satellites, vehicles, and sensors to calculate traffic flow, road closures, and alternative routes.
In 2024, Google reported that its live traffic models update over 20 billion kilometers of routes per day, helping drivers avoid congestion. Beyond convenience, this also reduces carbon emissions by shortening travel time and fuel use.
City planners rely on this same data to improve public transport routes and reduce bottlenecks, proving that the GIS behind your morning commute benefits entire cities.
Also Check: Application of Remote Sensing and GIS in Transportation
2. Online Deliveries and Ride-Hailing
Every time you order dinner or a taxi, GIS links your location with nearby drivers and delivery partners.
Apps like Uber, Bolt, and Deliveroo use GIS to calculate real-time distance, predict delivery times, and optimise route assignments. By analysing live traffic and weather conditions, GIS ensures efficient journeys even in peak hours.
A 2024 logistics study found that companies using GIS-based routing cut delivery costs by up to 18%, proving how spatial data improves both customer experience and operational performance.
3. Weather Forecasting and Disaster Alerts
Weather apps and early-warning systems depend on GIS to make forecasts more accurate.
Meteorologists combine satellite imagery, radar data, and terrain models to visualise rainfall, temperature, and wind speed.

When a cyclone forms, GIS overlays the storm’s path with maps of towns, schools, and hospitals, allowing authorities to plan timely evacuations.
In 2025, the Japan Meteorological Agency used GIS-based flood mapping to issue precise, district-level warnings, reducing casualties during heavy typhoons. These real-time spatial models save lives by predicting not only when disasters strike, but also where their impact will be worst.
4. Urban Planning and Smart Cities
Modern cities depend on GIS to plan infrastructure that meets community needs.
Urban planners use spatial data to decide where to build roads, transport hubs, and public spaces. GIS reveals patterns of population growth, land use, and commuting trends, essential for creating cities that are sustainable and accessible.
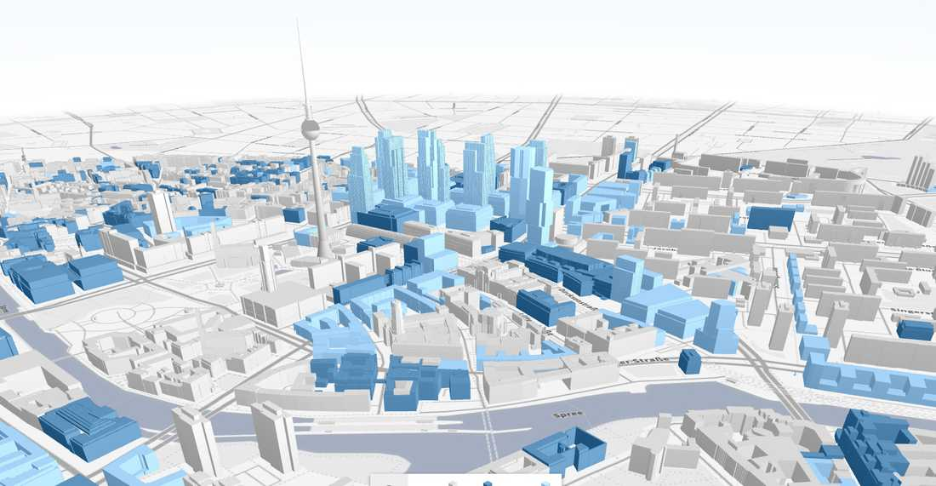
For example, the City of London’s Urban Data Platform (2024) integrates GIS with transport, energy, and housing data to support greener development. Similar systems in Singapore and Dubai are creating “digital twins”, 3D GIS models that mirror real cities and simulate future growth.
Want to use location data to improve daily operations or citizen services?
Work with GIS Navigator to build clear, reliable maps that support faster, smarter decisions.
📞 Schedule a Call | 📩 Email Us | 💼 Contact Us
5. Public Health and Disease Tracking
GIS is vital for healthcare planning. It helps health agencies track outbreaks, plan vaccination drives, and assess hospital accessibility.
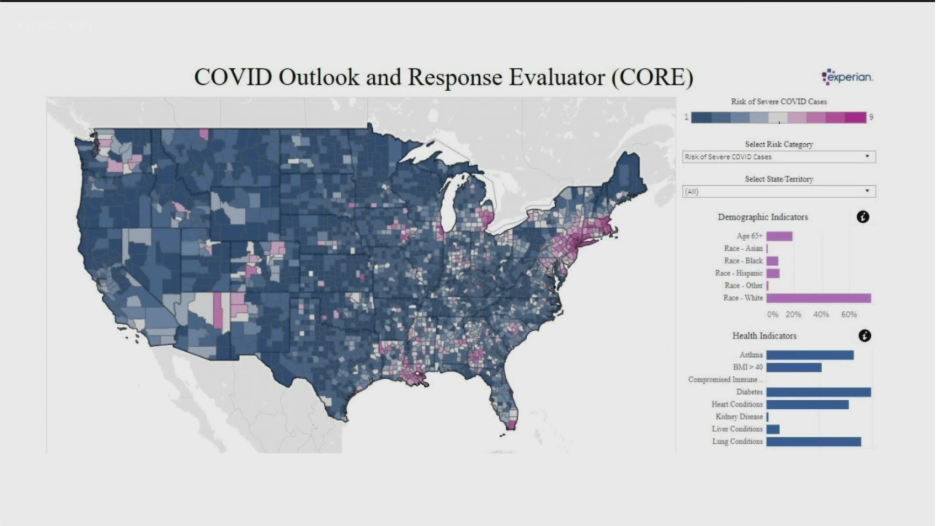
During COVID-19, GIS dashboards helped countries monitor cases by region. Now, that same technology is used for diseases like malaria, cholera, and dengue.
The World Health Organization (WHO) relies on GIS to predict mosquito-borne disease patterns using weather and terrain data. In Africa and Southeast Asia, these models guide targeted interventions, ensuring resources reach the most at-risk populations.
GIS doesn’t just map illness, it helps prevent it.
6. Agriculture and Food Production
Farmers worldwide use GIS to improve yield, cut waste, and adapt to climate change.
By analysing soil quality, rainfall, and temperature, GIS helps identify which crops suit which areas. Drones and satellite imagery provide field-level data for irrigation and fertilisation schedules.
In 2024, the European Space Agency and FAO expanded GIS-driven “smart farming” projects across Kenya and India, boosting yields by up to 22% and reducing fertiliser waste. GIS allows even small-scale farmers to plan smarter, making agriculture more sustainable and profitable.
7. Real Estate and Property Planning
When buying or developing property, location defines value, and GIS helps reveal why.
Estate agencies and developers use GIS to assess neighbourhood amenities, flood zones, and transport links. Governments also use GIS for land registration, zoning, and tax planning.
For example, the UK Land Registry integrates GIS with cadastral data, making boundary disputes easier to resolve. GIS adds transparency, helping buyers, investors, and city councils make informed decisions about land and housing.
8. Environmental Protection and Climate Action
Protecting nature begins with understanding it, and GIS makes that possible.
Environmental scientists use GIS to monitor deforestation, track endangered species, and assess pollution sources. The World Wildlife Fund (WWF) uses GIS to map elephant migration routes in Africa to prevent human–wildlife conflict.
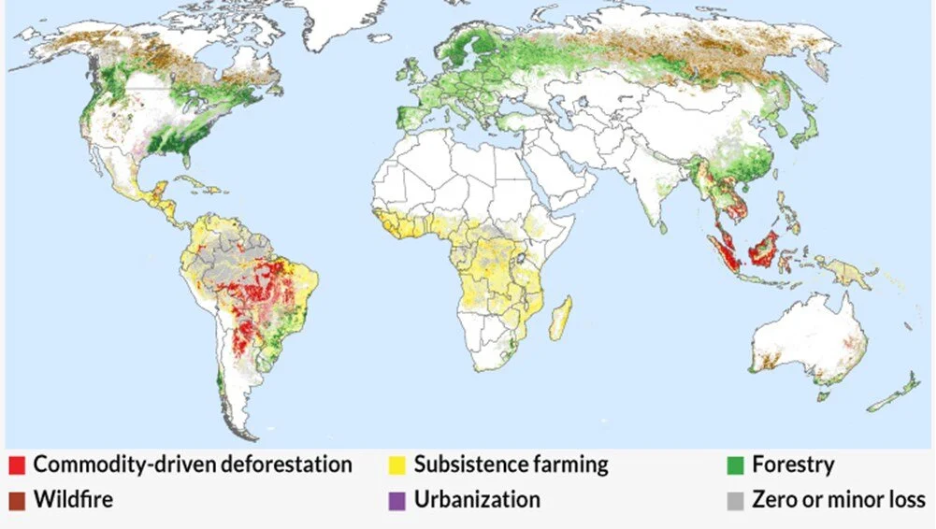
Governments use similar tools to identify renewable-energy potential, measure carbon emissions, and manage coastal erosion. The European Union’s Copernicus Programme uses GIS-based Earth observation data to guide climate adaptation across member states.
From forests to oceans, GIS turns global conservation into a measurable effort.
9. Emergency Response and Public Safety
When emergencies happen, seconds matter, and GIS helps save them.
Police, fire, and ambulance services rely on GIS to locate incidents, plan routes, and allocate teams. In the UK, the National Emergency Coordination Service uses GIS to identify the nearest available responders during crises.
During the 2023 Morocco earthquake, international rescue agencies used GIS-based satellite mapping to locate survivors and damaged zones within hours. These spatial tools help transform chaos into coordinated action.
Looking to strengthen response times or track incidents more accurately?
Let our GIS team help you map risks, routes, and resources in one connected platform.
📞 Schedule a Call | 📩 Email Us | 💼 Get a Quote Now
10. Education and Learning
GIS has entered classrooms as a practical teaching tool. Students use it to explore geography, history, and environmental change through visual learning.
Platforms like ArcGIS for Schools allow teachers to build interactive lessons that show climate trends, urban growth, or migration routes.
In 2025, the UNESCO Geo-Education Initiative introduced GIS-based learning kits in over 30 countries, improving geographic literacy and spatial awareness for millions of students.
GIS helps young people understand the world not just as a map, but as a living, changing system.
11. Waste Management and Recycling
Cities use GIS to optimise waste collection routes and recycling networks.
By mapping bin locations, road accessibility, and population density, local councils can reduce fuel use and collection time. For example, Amsterdam’s Smart Waste Program uses GIS and IoT sensors to track bin levels and schedule pickups only when needed, cutting emissions and costs.
These simple but data-driven changes make cities cleaner and operations more efficient.
12. Tourism and Cultural Heritage
Tourism boards use GIS to promote attractions and manage visitor flow responsibly.
By analysing visitor patterns, GIS helps protect natural and cultural sites from over-tourism. The Italian Ministry of Culture uses GIS to monitor foot traffic at UNESCO heritage sites like Venice, balancing tourism with preservation.
GIS also powers navigation in travel apps, virtual museum tours, and location-based storytelling, turning maps into experiences.
Why GIS Matters in Everyday Life
GIS may not be visible, but it shapes nearly everything we depend on, transport, safety, shopping, farming, healthcare, and education. It makes systems more connected and decisions more informed.
In an age where cities are growing and resources are shrinking, GIS helps people live smarter, whether that means avoiding a traffic jam or preparing for a flood.
It bridges the physical and digital worlds, turning everyday actions into coordinated systems that save time, reduce waste, and improve lives.
Ready to apply GIS to make your workflows more efficient and easier to manage?
Start your project with GIS Navigator and turn everyday location data into practical results.
📞 Schedule a Call | 📩 Email Us | 💼 Contact Us
Conclusion
From the moment you check the weather in the morning to when you share your location at night, GIS supports every part of your day. It powers the maps you trust, the services you rely on, and the systems that keep cities running.
It’s not just a mapping tool, it’s an invisible framework connecting people, places, and purpose.
At GIS Navigator, we help organisations apply GIS where it matters most, improving decisions, efficiency, and environmental awareness.
Reach out to explore how location intelligence can bring clarity to your operations and everyday workflows.