What is geospatial data analysis, and why are many organizations incorporating it into their analytics and other operations? We’ll answer these questions and more as we look at benefits of using geospatial data in analytics.
But before progressing any further, let’s first explore what is geospatial data analysis.
Struggling to Extract Value from Your Data? GIS Navigator helps you turn location-based data into actionable insights, improving efficiency and decision-making.
📞 Schedule a Call | 📩 Email Us | 💼 Get a Quote Now
What is Geospatial Data Analytics?
Geospatial data analysis involves collecting, combining, and visualizing various types of geospatial data. It is used to model and represent how people, objects, and phenomena interact within space, as well as to make predictions based on trends in the relationships between places.
Put another way, geospatial data analytics puts data in a more accessible format by introducing elements of space and time. Information that would be difficult to get out of reading line after line in a table or spreadsheet becomes much easier to understand in the context of a visual representation of what the world really looks like. This allows people to more easily pick up on patterns such as distance, proximity, density of a variable, changes over time, and other relationships.
In short, geospatial data analysis is about going beyond determining what happens to not only where and when it happens, but also why it happens at a specific place and/or time.
The Benefits of Using Geospatial Data in Analytics
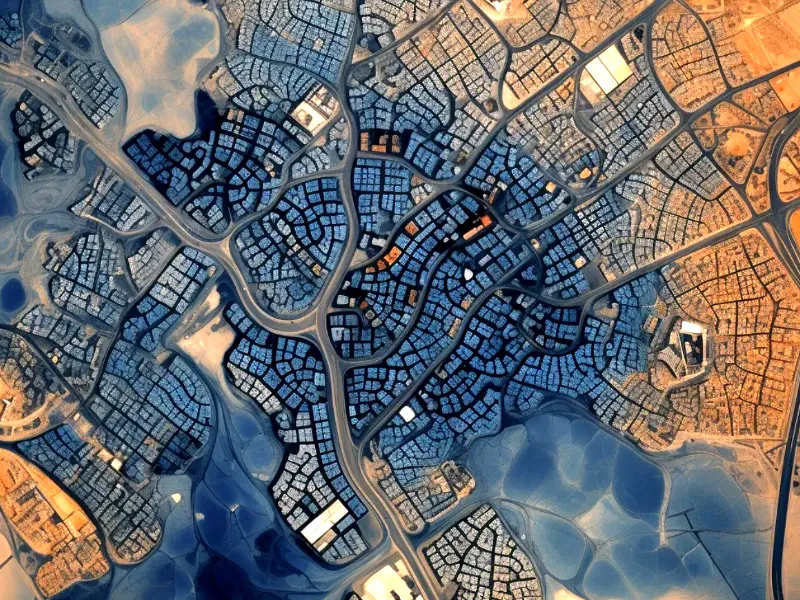

Integrating spatial thinking in the decision-making process has various benefits. Spatial and temporal patterns in large data sets are easier to spot with the help of geospatial data analysis. This approach has several benefits compared with the study of datasets stripped of any context.
Identification of spatial patterns and trends
It is a challenge to understand specific linkages and connections without considering ‘where’ (or ‘when’) they are happening. Geospatial data analysis helps to identify trends by bringing historical data into consideration.
Real-world modelling
Data analysis without location lacks a crucial element. Governments, entities, or businesses can model the physical environment, often in real time, with the help of geospatial data. Thus, simulating the real world helps to understand issues better and arrive at suitable solutions.
Segmentation
When GIS data becomes part of an analysis, you can create segments and filters depending on geography, which makes the overall study more specific.
Accurate forecasts
When you examine an event over time in the context of a particular region, you begin to comprehend why, where, and when it occurs. This improves your ability to forecast events, plan appropriate responses, or influence future events.
The several applications of geospatial data analysis underline the benefits of this technology and its ever-widening scope.
Geographical monitoring and first response
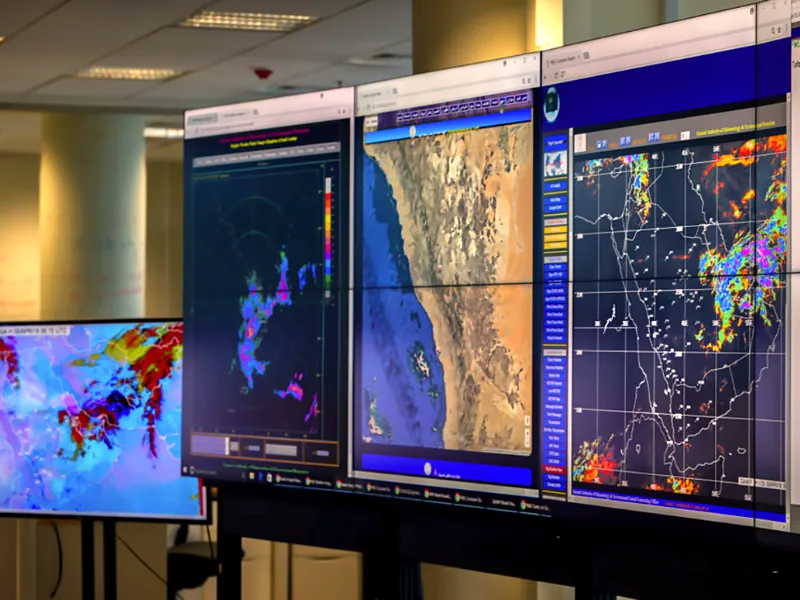

GIS data analytics is extensively used in monitoring changing geographies through spatial and temporal studies as done with biodiversity areas. It is also a source of reliable information and insights during emergencies and crises.
Geospatial data analysis helps create contingency plans in rescue operations during natural disasters such as floods, volcanic eruptions, and wildfires.
Want to Optimize Business Operations with Geospatial Data?
GIS Navigator provides advanced GIS solutions that help you streamline logistics, track assets, and gain deeper location intelligence.
📞 Schedule a Call | 📩 Email Us | 💼 Get a Quote Now
Humanitarian relief
GIS data studies help create policies for improving life in various regions by monitoring living conditions, sanitation, and access to basic amenities. Moreover, for food safety, geospatial data is extensively used to help farmers to optimise land use and improve yield.
Green initiatives
As the impact of climate change increases around us, finding solutions to mitigate risks come from geospatial data analytics. IoT provides area intelligence that can support green initiatives and innovation, such as better land use and transportation routes.
Communication
Geospatial data is vital to mapping communication networks and fixing problems or finding new regions for expansion. By mapping regional signal propagation along with data traffic and demographic, telecom businesses can plan their network-building strategies.
Cost efficiency
Geospatial data’s direct benefit to the business is growing as more businesses adopt and integrate geospatial data analysis into their growth strategies. It can improve the cost efficiency of businesses by streamlining supply chain management with real-time data of mobile assets.
Moreover, businesses can reduce overheads and improve efficiency by monitoring facilities with GIS data and using digital twins for forecasting. It also assists in determining footfalls in a specific area, competition in the target space, and demographics to improve the chances of seeking successful business opportunities.
Insurance and risk management
Whether it is agricultural insurance or risk management of assets and supply chains, geospatial data analytics can enhance visibility and transparency for creating policies, pricing them appropriately, and avoiding fraud.
For organisations on the digital transformation journey, agility is key in responding to a rapidly changing technology and business landscape. Now more than ever, it is crucial to deliver and exceed organisational expectations with a robust digital mindset backed by innovation. Enabling businesses to sense, learn, respond, and evolve like living organisms will be imperative for business excellence.
Ready to Make Smarter, Location-Based Decisions?
GIS Navigator delivers powerful geospatial analytics, helping you stay ahead with data-driven strategies.
📞 Schedule a Call | 📩 Email Us | 💼 Get a Quote Now
How can GIS Navigator help?
GIS Navigator has deep domain expertise, innovation, and experience in addressing client challenges and delivers focused technology practices with a global delivery model, integrated domain excellence, and complete turnkey solutions.