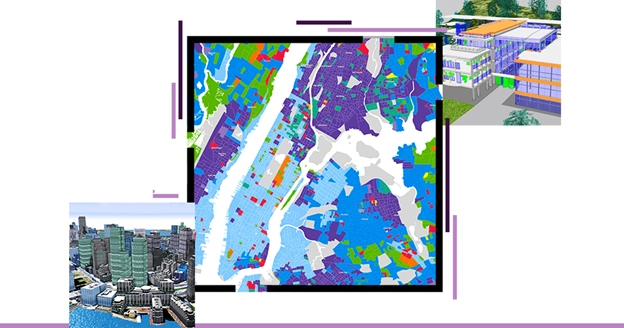
What is GIS and its Application?
Geographical data is one of the most abundant types of data available, forming the foundation for almost every application of geography. It pertains to the Earth’s surface, climate, ecosystems, and human activity factors that make up a typical GIS application. By visualising and making sense of this data, geographic information systems (GIS) assist individuals and organisations in comprehending the connections and patterns found in our environment.
If you’ve ever wondered what is GIS application, it refers to any practical use of geospatial data and technology to solve real-world problems, from disaster response to customer mapping.
GIS undertakes a spatial analysis of geospatial datasets comprising raster data (cells containing spatial information) and vector data (points, lines, and polygons) to create linked visualisations. Geographical factors such as location, natural resources, streets and buildings, and demography are displayed in these maps, graphs, statistics, and cartograms. What you see when you route a trip on Google Maps is the most iconic instance of a GIS visualisation.
Looking for Smarter Ways to Use Geographic Data?
GIS Navigator provides tailored solutions to turn complex spatial information into actionable insights.
📞 Schedule a Call | 📩 Email Us | 💼 Get a Quote Now
Real-World GIS Applications Across Industries
What are the applications of GIS? Geographic information system applications are as follow:
Weather Forecasting
As extreme weather events rise in intensity and frequency across the globe, planning and preparing for them is vital for governments and organisations alike. Organisations may make weather-related data actionable using software solutions that integrate geospatial data, GIS mapping, and advanced environmental analytics. Real-time data and digital maps are used in more precise forecasts to help businesses anticipate and react to weather occurrences more effectively, which lessens the impact on operations.
Learn how we support better forecasting and risk management.
👉 Explore Our Satellite Image Processing Services
Enterprise Decision-Making
GIS software makes strategic business decisions possible in various domains, including customer segmentation, real estate portfolio management, transportation and delivery management, and more.
Businesses use geographic information system (GIS) technology, for instance, to ensure personnel and equipment are located on or off campus. When field service management (FSM) incorporates GIS, artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), cloud, and mobile technologies, field service technicians have access to the most recent information. Effective field service management lowers costs and increases customer happiness by ensuring personnel respond promptly to and handle customer issues.
Agriculture
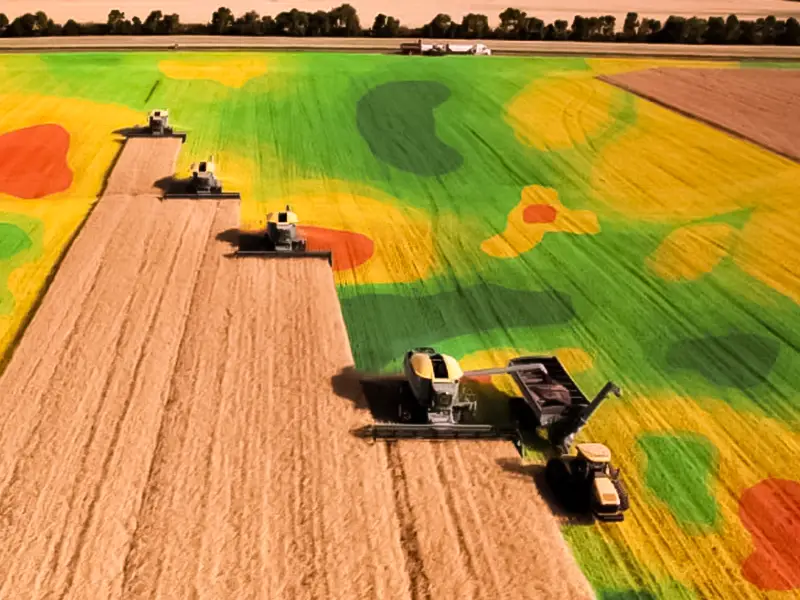

GIS technology provides precise, thorough data, enabling productive and sustainable farming. Knowledge of how changes in land affect crop health and where particular crops will thrive enhances decision-making and crop management.
For instance, smallholder farms are essential to a stable global food supply but also face unique risks from climate and weather-related factors. The Plan21 Foundation and IBM developed a technology solution demonstrating how insights from several sources, such as weather and agronomic data, help farmers better adapt to climate change. Go here to learn more about the initiative.
Discover how our Environmental Monitoring & Agriculture solutions can enhance your projects and contribute to a sustainable future.
Furthermore, Texas A&M AgriLife and IBM have developed a technology to enhance crop management techniques. To determine when and how much water crops require, inexpensive sensors are buried in the soil to monitor temperature and moisture content. This soil and water analysis data helps farmers cut expenses and pollution runoff while increasing yields.
Utilities
Using GIS technology and geospatial data, utility businesses can more effectively anticipate, plan for, and recover from severe weather disasters. This reduces power outages and speeds up restoration times. By gaining insight into networks, utility businesses may increase operational efficiency and reliability for traditional and renewable energy sources, independent of weather conditions.
Utility firms can optimise their operations by leveraging location intelligence to comprehend demand patterns based on weather.
Utility firms can also check thousands of kilometres of electrical lines with GIS technology to ensure they operate at peak efficiency. Preventative maintenance and worker schedule optimization can reduce downtime and increase customer satisfaction.
Explore our Infrastructure & Utilities Services to enhance your projects’ efficiency and sustainability.
Climate Change
Geographic Information System (GIS) technology offers a comprehensive perspective of present and future environmental challenges, making it a valuable weapon in the battle against climate change. Detailed visualisations help organisations monitor risks, foresee possible problems, and search for solutions.
For example, GIS technologies help scientists better understand shifting weather patterns, thereby assisting governments and organisations in making more informed strategic decisions. Thanks to intelligence-based data and satellite images, first responders and recovery personnel are deployed where needed; once the crisis has passed, GIS can help restore services and structures.
In addition, queries such as “Where is the best place to put a wind farm?” are becoming increasingly common as governments and organisations try to lessen their carbon footprint. GIS and geographic data can be used to answer questions like “Does this building receive enough sunlight to install solar panels?”
Tackle Climate Challenges with GIS
👉 Explore Our Environmental Monitoring & Agriculture Services
Urban Planning
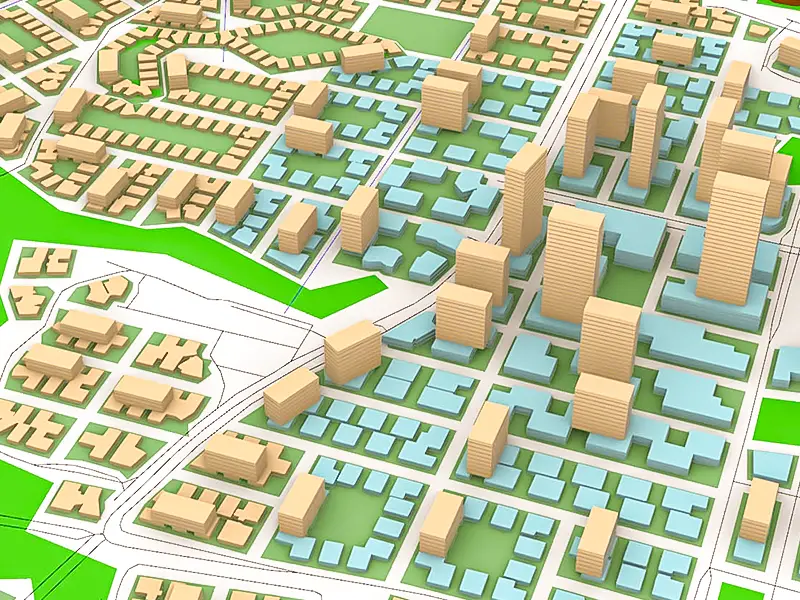
Urban planning is one of the most impactful areas where GIS application continues to shape infrastructure, zoning, and public service delivery.
Urban planning includes:
- Zoning and land use projects.
- Responding to natural disasters and health events.
- Designing buildings and highway systems.
- Producing energy.
- Managing waste and resources.
- Producing power
Learn more about how we’re supporting Urban Planning & Development projects.
Governments employ GIS data and GIS-based solutions for urban planning. Planners in California, for instance, use technologies that combine satellite imagery, vector data, and remote sensing to create disaster response plans and the best locations for fire hydrants. California is prone to wildfires. The State of Arizona uses GIS technology to manage its more than nine million acres of land portfolio.
Forestry
Although GIS’s functions in urban planning may appear diverse, they are surprisingly diverse in forestry. In general, GIS helps in forest management. However, it can come in a variety of shapes and sizes.
Timber businesses have used GIS to identify the most profitable forest portions for harvesting and optimise their revenue. Nonetheless, governmental and commercial enterprises have used the technology to prepare for wildfires, evaluate the characteristics of different vegetation types, adhere to environmental laws, and protect other species’ forest habitats.
Ready to Improve Your Forest Management Strategy?
👉 Explore Our Environmental Monitoring & Agriculture Services
Crime Mapping
What is GIS used for by police (and emergency services) …
- Obtaining, analysing, and displaying crime data to pinpoint locations for quick response deployments. Depending on the traffic volume and the time of day, cars may need to be positioned closer to areas known for high-traffic accidents.
- Presenting crime data according to the type of incident and the time of day to forensically and continuously comprehend emerging patterns in crime.
- Police and other agencies are dispatched to a specific area (911 & 000 calls).
- Establishing exclusion zones for sexual offenders near playgrounds and educational institutions (mainly when linked with GPS surveillance)
- Utilising geographic profiling of a string of related crimes to pinpoint the potential location of a criminal.
Looking to Enhance Decision-Making with Spatial Data?
Our GIS solutions provide in-depth spatial analysis, empowering you to make informed decisions.
📞 Schedule a Call | 📩 Email Us | 💼 Get a Quote Now
How Can GIS Navigator Help You with GIS Solutions for Your Business?
Upon determining that your company needs a GIS application, you must assemble a committed development team. For more than a decade, GIS Navigator has provided cutting-edge mapping solutions. Our group is prepared to tackle the latest technological challenges because it has completed and implemented numerous GIS projects in various industries.
Throughout our team, you will encounter specialists in specific domains constantly seeking the most recent advancements in mapping techniques.
We offer data analysis, web app development, indoor mapping, and cartography for specialised mapping projects. Regardless of the type of project and its difficulty level, we can identify the most suitable solution to meet your company’s objectives.
Ready to Transform Your Operations with GIS Technology?
GIS Navigator specializes in integrating GIS into various industries, optimizing processes and outcomes.
📞 Schedule a Call | 📩 Email Us | 💼 Get a Quote Now
Conclusion
It is now evident that GIS solutions have been extensively used across various sectors. GIS data is being used in over 1,000 different areas, which will only rise.
Now that the applications and uses of GIS have been evaluated, businesses can see the benefits of mapping databases and data sets. GIS data is being integrated everywhere, from waste management, aviation, archaeology, and geology to asset management and finance.
This technological solution is unique in today’s market since, if implemented, it can significantly alter or even slightly optimise the development of the entire industry.
Now that the GIS applications and practical uses have been evaluated, it’s easier to see how they support every major application of geography, from environmental conservation to modern urban planning.
We are always available to assist you if you have any more questions about the creation and application of GIS! Speak with the GIS Navigator staff right now to get the best mapping options for your company!