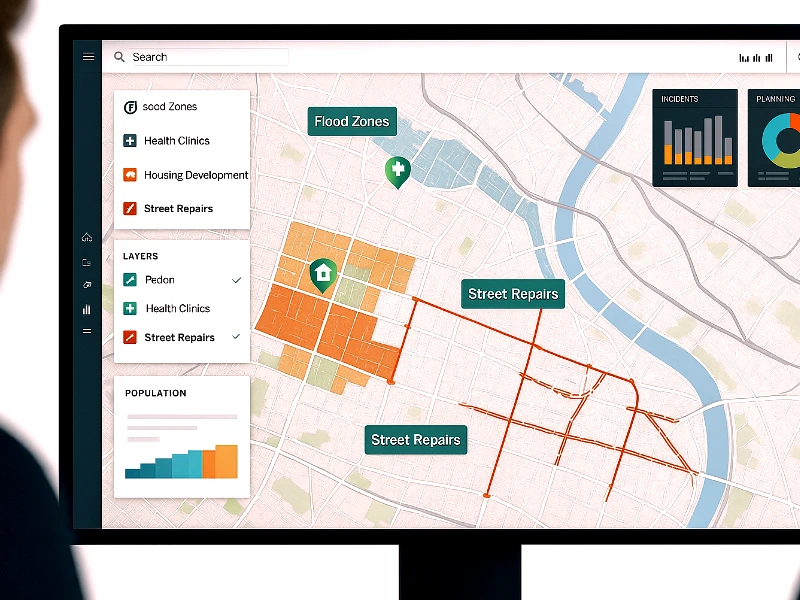
What is Digitization in GIS?
What is digitizing in GIS? Simply put, it is the process of converting geographic data into a digital format, which is essential for the functioning of Geographic Information Systems (GIS). This process, known as map digitization, is essential for creating accurate, editable, and shareable spatial data. Once complete, the output is a digitized map that can be analysed, layered, and integrated into GIS software. This transformation involves digitizing map features by tracing spatial data on paper or scanned images into digital points, polylines, or polygons. GIS digitization facilitates recording, displaying, and analysing geographic information, generating map layers, and storing data for various applications. This article delves into the process of GIS digitization, outlining the different methods, common errors, and the overall importance of digitizing geographic data.
Need Professional GIS Digitization Services?
Let our experts handle your data conversion with precision and accuracy!
📞 Schedule a Call | 📩 Email Us | 💼 Get a Quote Now
Types of Digitization in GIS

There are three primary methods of digitizing: Manual Digitizing, Heads-up Digitizing, and Automatic Digitizing. Each method has its unique processes and applications, which are detailed below.
1. Manual Digitising
Manual digitizing in GIS involves tracing geographic features by hand using a digitizing tablet and a puck (a device similar to a mouse). This method is used when we need high accuracy and precision but we don’t use it most often now a days. The data digitization process includes the following steps:
- Preparation: Set up the digitizing tablet and secure the map or image.
- Tracing: Use the puck to trace the features on the map, converting them into digital points, lines, or polygons.
- Verification: Cross-check the digital data against the original map to ensure accuracy.
Manual digitizing is beneficial for detailed work, such as creating maps for urban planning or environmental studies.
2. Heads-up Digitising
Heads-up digitizing, also known as on-screen digitizing, involves scanning paper maps into digital images and then tracing the features directly on a computer screen. This method is advantageous because it:
- Preserves Original Documents: The original paper maps are not altered or damaged during the process.
- Efficiency: Digital tracing on a computer screen is faster and more flexible than manual digitizing.
- Accessibility: Allows for easy editing and updating of digital maps.

However, heads-up digitizing is limited by the resolution of the scanned images and may not capture fine details as accurately as manual digitizing.
3. Automatic Digitising
Automatic digitizing converts raster images (scanned maps or satellite images) into vector data using specialized software. This method is highly efficient for handling large datasets and involves:
- Raster-to-Vector Conversion: Software algorithms detect and trace the boundaries of features in the raster image.
- Data Management: Organizing and managing the digitized data for analysis and mapping.
- Real-time Updates: Automatic digitizing can provide up-to-date spatial data, essential for applications such as real-time monitoring of environmental changes.
Automatic digitizing is commonly used in applications requiring extensive data collection, such as topographic mapping and land use planning.
Need GIS Support for Your Digitisation Project?
Let GIS Navigator handle your digitisation needs with precision and efficiency. Our services are designed to transform your data into actionable formats that drive smarter decision-making.
Here’s what we offer:
1. Accurate georeferencing and digitisation of paper maps and scanned drawings
2. Fast turnaround for high-volume digitisation projects
3. Clear, editable formats ready for use in GIS platforms
4. Consistent quality checks for reliable outputs
5. Flexible solutions tailored to your project needs
6. Support for spatial data conversion and mapping
Get in touch with us today to discuss your digitisation project.
📞 Call Now | 📩 Email Us | 💼 Get a Free Quote
Or explore
👉 Georeferencing & Digitisation Services
Steps of Digitization in GIS
Digitizing data in Geographic Information Systems (GIS) is essential for creating maps, analysing spatial information, and managing geographic data effectively. Here’s a general process to follow for data in digitization in GIS:
- Source Data Collection: The first step involves collecting the geographical data that you intend to digitize. This data can come from various sources such as satellite images, aerial photographs, existing maps, GPS data, and field surveys.
- Setting Up the GIS Project: Start by setting up a new project in your GIS software. This includes defining the coordinate system, setting the scale, and ensuring that all data layers will align correctly during the digitization process.
- Scanning and Georeferencing: If you’re working with hardcopy maps or images, you need to scan them into a digital format. Once scanned, these images must be georeferenced, meaning they are aligned with a coordinate system so that each point on the image can be associated with a geographic location on the earth’s surface.
- Digitizing the Data: Manual Digitizing involves using tools within GIS software to trace features from georeferenced maps. Typically, a mouse is used to manually trace elements such as roads, boundaries, or rivers, converting them into vector formats like points, lines, or polygons. On the other hand, Automatic Digitizing, or Vectorization, allows some advanced GIS software to automatically convert raster images (like scanned maps) into vector data. This automatic process uses color, intensity, or other thresholds but often requires subsequent clean-up and refinement to ensure accuracy.
- Editing and Cleaning Up: After the initial digitization, the data often requires editing to correct errors, remove duplicates, and refine shapes. Tools within GIS allow for editing vertices, snapping lines and points together, and correcting topological errors such as overlaps or gaps.
- Attribute Data Entry: Adding attribute data is crucial as it provides information about the map features. This might include names, classifications, descriptions, or quantitative values. Attribute data can be entered manually or imported from databases.
- Data Integration and Analysis: Once digitized, the new vector layers can be integrated with other geographic data layers for comprehensive analysis and interpretation. This integration allows for spatial analysis, modelling, and decision-making based on multiple data sources.
- Quality Assurance and Validation: It’s important to validate the digitized data to ensure its accuracy and usability. This includes checking for accuracy against control points or reference data, performing statistical checks, and field verification.
- Output and Distribution: Finally, the digitized data can be used to produce maps, reports, or be shared across different platforms or among various stakeholders. Ensure that the data is compatible with other systems and adheres to data sharing and privacy standards.
Each GIS project might require specific tools or steps depending on the complexity of the data and the intended use of the digitized information. Always ensure you have the right software and training to handle GIS data effectively.
Types of Digitizing Errors in GIS
Digitizing errors can occur during the conversion process, affecting the accuracy and reliability of the digital data. Common digitizing errors include:
1. Geodetic Errors
Geodetic errors in GIS stem from inaccuracies in measuring geographical coordinates, often due to factors affecting GPS signals like atmospheric conditions, multipath reflections, and satellite geometry.
For example, when mapping a national park boundary using GPS, these errors might misplace the boundary line several meters from its actual location, affecting legal boundaries and resource management. Mitigating these errors involves techniques like using differential GPS, improving satellite positioning, and correcting for environmental effects to enhance data accuracy.
2. Dangling Nodes
Dangling nodes are points that are not connected to other parts of the network, resulting in incomplete or inaccurate representations of features.
3. Switchbacks, Knots, and Loops
These errors occur when extra vertices or nodes are added during digitizing, causing the lines to form unintended bends, knots, or loops. These issues can distort the spatial representation of features.
4. Overshoots and Undershoots
Overshoots happen when the digitized line extends beyond its intended endpoint, while undershoots occur when the line falls short. Both errors can cause inaccuracies in map features and affect spatial analyses.
5. Silver Polygons
Silver polygons are small, unwanted polygons formed between adjoining polygons due to inaccuracies in snapping tolerance. These errors can complicate spatial analysis and data management.
Importance of GIS Digitization
Digitization is a crucial process for GIS professionals as it transforms physical maps and analogue data into digital formats that are easier to manipulate, analyse, and store. The benefits of GIS digitization include:
Enhanced Data Accuracy
Digitization improves the precision of spatial data, which is essential for accurate mapping and analysis.
Efficient Resource Management
Digital maps allow for better resource management by providing detailed spatial information that can guide decision-making processes in various fields, such as urban planning, agriculture, and environmental management.
Improved Accessibility and Flexibility
Digitized data is easily accessible and can be quickly updated or modified, enhancing the flexibility and efficiency of GIS operations.
Support for Sustainable Practices
Accurate digital maps support sustainable practices by enabling detailed monitoring and management of natural resources and human activities.
The increasing need for real-time data, automation, and cloud-based systems is driving the digital transformation in GIS. Organizations are moving from paper-based workflows to integrated digital platforms powered by digitization, spatial analytics, and mobile GIS applications. This shift not only enhances operational efficiency but also ensures that spatial data remains dynamic, accurate, and instantly accessible across sectors.
Advantages of Digitizing In GIS
The digital map has emerged as one of the most effective instruments for data analysis and surveying in various industries. Spatial data digitisation has become a crucial aspect of the work of urban planners and surveying geologists.
- It makes information easily accessible to managers and employees when needed.
- It is frequently simpler for businesses to make updates to a GIS file when an update or modification is required by importing the digital data into a PDF or JPG format.
- Additionally, when decision-makers require them, they can view maps in their favourite formats, such as PDFs and JPEGs.
🎯 Need High-Quality GIS Digitization?
Let’s turn your maps and spatial data into accurate digital formats!
📞 Call Now | 📩 Email Us | 💼 Get a Free Quote
Conclusion
The process of GIS digitization, from paper maps to digital data, is a vital step in modern geographic information systems. It enhances the accuracy, efficiency, and accessibility of spatial data, supporting a wide range of applications from environmental monitoring to urban planning. Understanding the methods and challenges of digitization helps GIS professionals to better utilize this technology for improved decision-making and resource management.
Are you ready to take your GIS capabilities to the next level? GIS Navigator offers cutting-edge digitization services that transform paper maps into precise, high-quality digital data. Whether you need manual, heads-up, or automatic digitizing, our team of experts ensures accuracy and efficiency, tailored to your project’s needs.