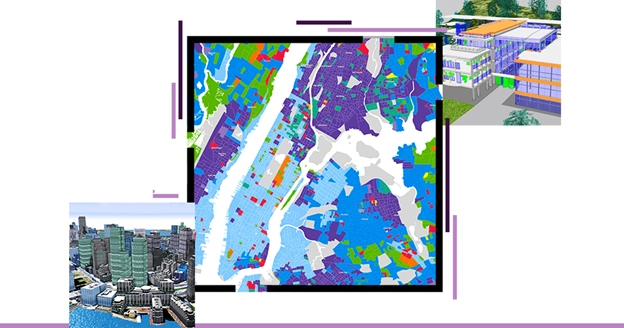
What is GIS Mapping for Water Utility Networks?
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) mapping is extremely crucial when it comes to managing and maintaining water utility networks. From careful asset management to efficient network modelling and analysis to water loss management, GIS plays a crucial role in enabling professionals to get things done the right way. By utilizing the detailed spatial data provided by GIS, engineers make informed decisions in the context of managing and optimizing water distribution networks. This not only allows for efficient management of resources but also ensures sustainable water distribution.
In addition to all things monitoring and management, GIS also allows engineers and other stakeholders to solve challenges such as water loss and leak detection. Moreover, professionals can also ensure on-point infrastructure maintenance by making the most of the data provided by GIS mapping.
Struggling with Water Network Management?
GIS Navigator helps you map, monitor, and optimize your water infrastructure with precision.
📞 Schedule a Call | 📩 Email Us | 💼 Get a Quote Now
Importance of Accurate Mapping in Utility Networks
Managing extensive underground and above-ground water infrastructure is as complex as it sounds. The interconnectedness of various systems not only requires thorough studying but the mapping has to be highly accurate too. All of that becomes easily manageable with the help of GIS.
Here is how: GIS mapping enables professionals to understand the scale and interconnectedness of the underground and above-ground water infrastructure. After carefully monitoring those complex systems, engineers can work on efficient mapping and management of water utility networks.
By doing so, challenges such as leak detection, corrosion, etc. can be easily resolved. In addition, infrastructure management also becomes easy when GIS is incorporated into understanding utility networks and allows fair distribution of resources among the masses.
Ensuring accurate mapping in utility networks and enhancing service reliability while keeping the operational costs as low as possible can be cumbersome. However, GIS Navigator enables utilities and engineers to do just that in a highly efficient manner.
For example; utility operators can monitor water infrastructure in real-time which helps them to manage assets in a more efficient and reliable manner. All the field data and network information can be brought into a single platform to be studied by the concerned teams who can, then make informed decisions accordingly.
Now, such high-scale monitoring and management can cost a lot but thanks to GIS Navigator, utility operators can detect leakage, pressure imbalances, etc. well before time. Once the issues have been identified, concerned teams are assigned to quickly resolve the challenges; ultimately allowing users to carry on with their day-to-day activities.
If you’re interested in learning more about how GIS Navigator can help your utility network, contact us today for GIS utility mapping services.
Key Components of GIS Mapping for Water Utility Networks
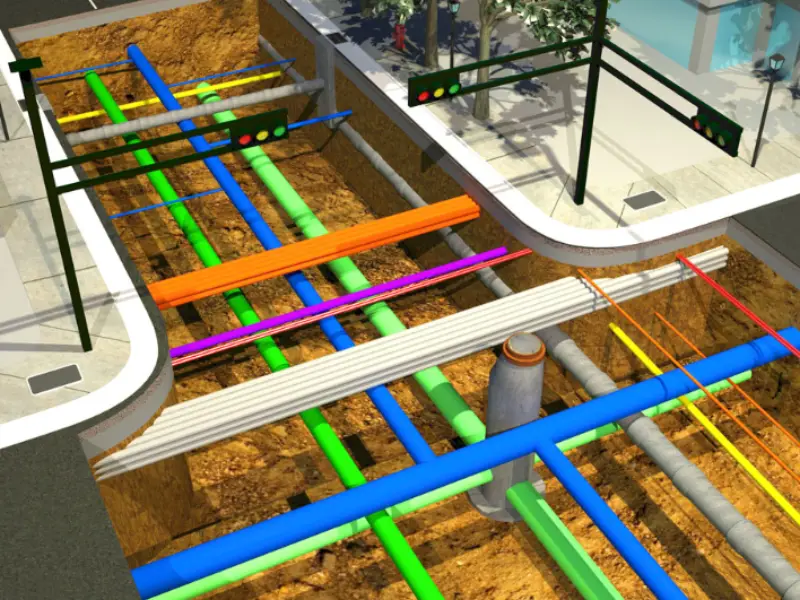
Geospatial Data: GIS allows utility operators, engineers, etc. to visualize the locations of various systems such as water pipelines, valves, meters and more. This becomes possible when the exciting records are integrated with spatial data. By utilizing the mapping technology, GIS offers highly precise surveys to ensure efficient management and maintenance of the water distribution networks.
Attribute Data: Every asset has attribute data to share with the concerned teams including utility operators and engineers. For example; a valve linked to its attribute data can show when was it installed in a system, its material specifications as well as other maintenance records. Such data is crucial to understanding complex water utility networks and maintaining records accordingly.
Spatial Analysis Tools: Maintaining water utility networks is one thing, monitoring and analysing them is another. GIS makes it easier for the stakeholders to analyse hydraulic performance while also monitoring other factors such as demand forecasting and detailed water flow analysis. After identifying imbalances in the systems, the stakeholders cannot only work on optimized water flows but can also plan on expanding infrastructures.
Suggested: What is spatial analysis in GIS?
Applications of GIS in Water Utility Networks
Water Network Optimization: Water network optimization gets the ball rolling in every sense of the word. Thankfully, GIS does all of that by enabling utility managers in multiple ways. For example; they can utilize GIS to maintain consistent water pressure across the network. In addition, they can also identify bottlenecks well before time and ensure improved service delivery in a given area.
Use of Hydraulic Models: GIS also allows using hydraulic models to simulate different water flow scenarios. Through real-world scenario simulation, utility managers can identify imbalances and inefficiencies that can lead to major disruptions in the system. GIS enables the stakeholders to counter such issues and maintain uninterrupted water flow.
Asset Management: GIS has proved to be instrumental in asset management. By making the most of the data provided by GIS, utilities can analyze the infrastructure in detail and then schedule timely repairs. In addition, GIS also allows efficient replacements of damaged assets to avoid disruptions and costly failures.
Leak Detection and Prevention: Using sensor data, GIS enables the stakeholders to identify leaks in the pipelines, valves, etc. and prompt immediate repairs. By doing so, utility managers can ensure seamless water flow. We must add here that GIS is not only beneficial in detecting leakages but also helps identify abnormal flow of water.
Emergency Response: GIS allows efficient monitoring and management in areas that are prone to natural disasters. In addition to that, it can also help utility operators to respond to challenges such as water main breaks and contamination. And that’s not it as GIS immediately alerts the stakeholders to make informed decisions to mitigate risks and reduce water loss. By utilizing the data provided by GIS, utility operators can locate damaged valves and then shut-off points during an emergency situation.
Regulatory Compliance: Utility operators and engineers can work on plans that are in compliance with the regulatory requirements. These requirements cover factors like quality monitoring, reporting, etc. In addition to that, GIS also simplifies the process of compliance reporting by providing automated GIS records.
Want to Reduce Water Loss and Improve Efficiency?
Use GIS Navigator’s advanced mapping solutions to detect leaks, plan maintenance, and streamline operations.
📞 Schedule a Call | 📩 Email Us | 💼 Get a Quote Now
Benefits of GIS for Water Utility Networks
Improved Decision-Making: Making informed decisions is an integral part of all sorts of planning. When it comes to water utility networks, the utilities and engineers are dependent on spatial data to chalk out everything from designing to maintaining the infrastructure and more. GIS data helps the stakeholders do so, that too with precision and accuracy; ensuring that the assets are managed wisely and no resources get wasted. By utilizing GIS data to its full potential, utility managers cannot only focus on the current systems and their maintenance but can also work on careful future expansions as well.
Cost Savings: Every project has a cost and then some additional cost to work with but that’s just that. When the project costs keep on increasing, then it can also become a liability. However, with GIS, additional operational costs can be reduced through optimized resource allocation. In addition, utility managers can also improve their work efficiency by monitoring the current systems in real-time.
Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: Customer satisfaction is highly crucial for any system to run well. GIS data not only helps in minimizing service disruptions but also offers improved communication between service providers and customers. The end customer can be informed about outages, repairs and system upgradation well before time to avoid clashes.
Sustainability and Resource Conservation: GIS mapping is not only a tool to efficiently use water resources but it also helps utilities and engineers to minimize the carbon footprints. This becomes possible by reducing water loss and promoting sustainable planning.
Related: Benefits of GIS in the utilities sector
Challenges in GIS Mapping for Water Utility Networks

Data Accuracy and Resolution: GIS mapping is a highly effective method to work on efficient water utility networks. However, even in GIS mapping, issues such as gaining accurate data can arise. The use of poor-quality data sources can result in obtaining inaccurate data which cannot only affect the GIS system but can also impact mapping for water utility networks.
Complex Terrain Analysis: Managing water utility networks in mountainous regions can become really difficult because the water pressure in such areas fluctuates more than usual. In addition, surveyors and utility operators can also face challenges such as accessing areas that are steep. Managing water sources in those areas requires advanced tools and meticulous planning.
Enhance Your Water Utility Networks with GIS Navigator!
Gain real-time insights, improve resource allocation, and ensure reliable water distribution.
📞 Schedule a Call | 📩 Email Us | 💼 Get a Quote Now
Case Study: GIS Navigator Solutions for Water Utility Networks
Comprehensive Network Mapping: GIS Navigator plays an essential role in helping utility operators work on crucial operations. Such as careful asset management, leak detection as well as network optimization. The utilities can utilize the existing records, integrate them with new data and then make informed decisions to continue the service without any disruptions in the system.
Hydraulic Modelling and Simulations: Water utility networks require improvement and constant expansions. And rightly so, as the population keeps on increasing in a given area, the demand will also increase. To meet the increased demands of water consumption, GIS Navigator enables the stakeholders to make the existing systems efficient and plan on future expansions through advanced modelling tools.
Emergency Response Solutions: As we have discussed earlier in the article as well, GIS Navigator allows water utilities in several ways. Such as they can detect pipeline breaks, blockages and pressure drops through accurate data visualization in real time. After such issues have been identified, response efforts can be streamlined. By doing so, faster repairs can be managed without causing long-term disruptions in the water flows.
Are you working on a project that requires GIS mapping for water utility networks? Our expert teams are highly qualified to guide and assist you in doing just that. Feel free to get in touch with us today and we’ll take it from there!