Geographical Information System (GIS) is a computer system that analyses and collects visual as well geographical data by transforming complex data sets into actionable insights. GIS plays a critical role in natural resource mapping and management by offering powerful tools to visualise, analyse and interpret data related to Earth’s resources. By integrating layers of information about biological, physical, and human-made systems, GIS technology helps users better comprehend patterns, trends, and relationships across different landscapes.
When it comes to natural resource management, GIS has turned out to be indispensable. It helps organizations monitor, assess and most importantly sustainably manage resources such as forests, water, minerals and wildlife. By offering precise mapping, predictive modeling and real-time data analysis GIS is an important asset for informed decision-making in order to balance conversation alongside resource utilization.
Sustainable resource management has become fundamental. Global warming, climate change, deforestation and the depletion of natural resources pose significant challenges globally. GIS provides innovative tools to solve these pressing issues. With its advanced capabilities GIS ensures efficient planning, proactive risk management and environmental sustainability.
Seeking Effective Natural Resource Management Solutions?
Utilize GIS Navigator’s solutions to monitor ecosystems, manage resources sustainably, and enhance conservation efforts.
📞 Schedule a Call | 📩 Email Us | 💼 Get a Quote Now
Application of GIS in Natural Resource Management
GIS serves as a transformative tool when it comes to natural resource management, providing diverse applications that address resource optimisation alongside the need for conservation and sustainable development. GIS plays a crucial role in various sectors.

Water Resource Management
Starting with water resources, GIS supports watershed management by mapping catchment areas, assessing the impact of land use for water flow and analysing drainage patterns. GIS helps in flood mapping by identifying high-risk zones and pro,lying mitigation by enabling better disaster preparedness. GIS also serves to be instrumental in monitoring water quality by assessing the spread of pollutants by firstly mapping them and eventually guiding cleanup strategies.

Forest Management
Moving on to forest management,GIS allows for monitoring of forest through satellite imagery and spatial analysis. It helps in detecting deforestation by identifying land cover changes that take place overtime. GIS tools also aid in detecting deforestation through the identification of overtime land cover changes. Which further allows for targeted reforestation efforts.
To continue, GIS tools further help in managing timber resources by estimating biomass, mapping the distribution of tree species and planning harvesting schedules that are sustainable. GIS is also used to analyze forest health, pest infestations, tracking if disease outbreaks and on a large scale the impacts of climate change on forest ecosystems.
Wildlife Conservation
Wildlife Conservation is enhanced through GIS by habitat mapping which identifies crucial areas for the survival of species. Furthermore, by tracking species migration patterns using the GPS integrated tool within GIS tools, conservationists can design corridors that connect fragmented habitats. Through the analysis of species distribution and identification of hotspots that require attention for conservation purposes GIS supports biodiversity protection. This helps in creating policies that minimize human-wildlife conflict and promote the preservation of endangered species.
Mineral & Energy Resources
Moreover, GIS supports mineral and energy resources. GIS maps and evaluates the accessibility of mineral deposits promoting sustainable extraction practices. When it comes to renewable energy projects GIS analyses potential sites for wind turbines, solar farms and hydroelectric power plants by using data on sunlight exposure, water flow, and wind patterns.
Related: GIS in Mining
Agriculture Planning
Lastly, agricultural planning is supported by GIS through the formation of precise and details maps on soil types, moisture levels and crop health that helps farmers in optimising the use of resources. GIS also aids in soil analysis and identifying nutrient deficiencies as well as erosion prone areas for better soil management, while also supporting crop yield optimization by integration pest information, weather data and irrigation planning to help farmers achieve optimum productivity while minimizing environmental impact.
By providing a wide range of applications GIS provides a foundation for fostering sustainable resource management and informed decision making globally.
Tools and Technologies within GIS
The use of GIS tools and technology helps users gain better insights from natural resource data.
The success of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) in natural resource management results from its advanced tools and use of additional technology systems. Users can process and display spatial data to make better decisions through these GIS tools.
Several GIS platforms are widely used for their robust capabilities and ease of use:
1. Google Earth Engine
This cloud-based system processes substantial spatial data collections with its platform. GIS provides exceptional value for tracking land use patterns and monitoring climate and disasters by accessing both Google satellite imagery and cloud processing power.
GIS becomes more effective when developers connect it to advanced technologies that collect better data and perform better analysis.
2. UAVs
High-resolution camera and sensor drones take clear aerial photos of land environments. GIS systems convert collected data into maps that show vegetation status and infrastructure while also making sense of hard-to-reach areas.
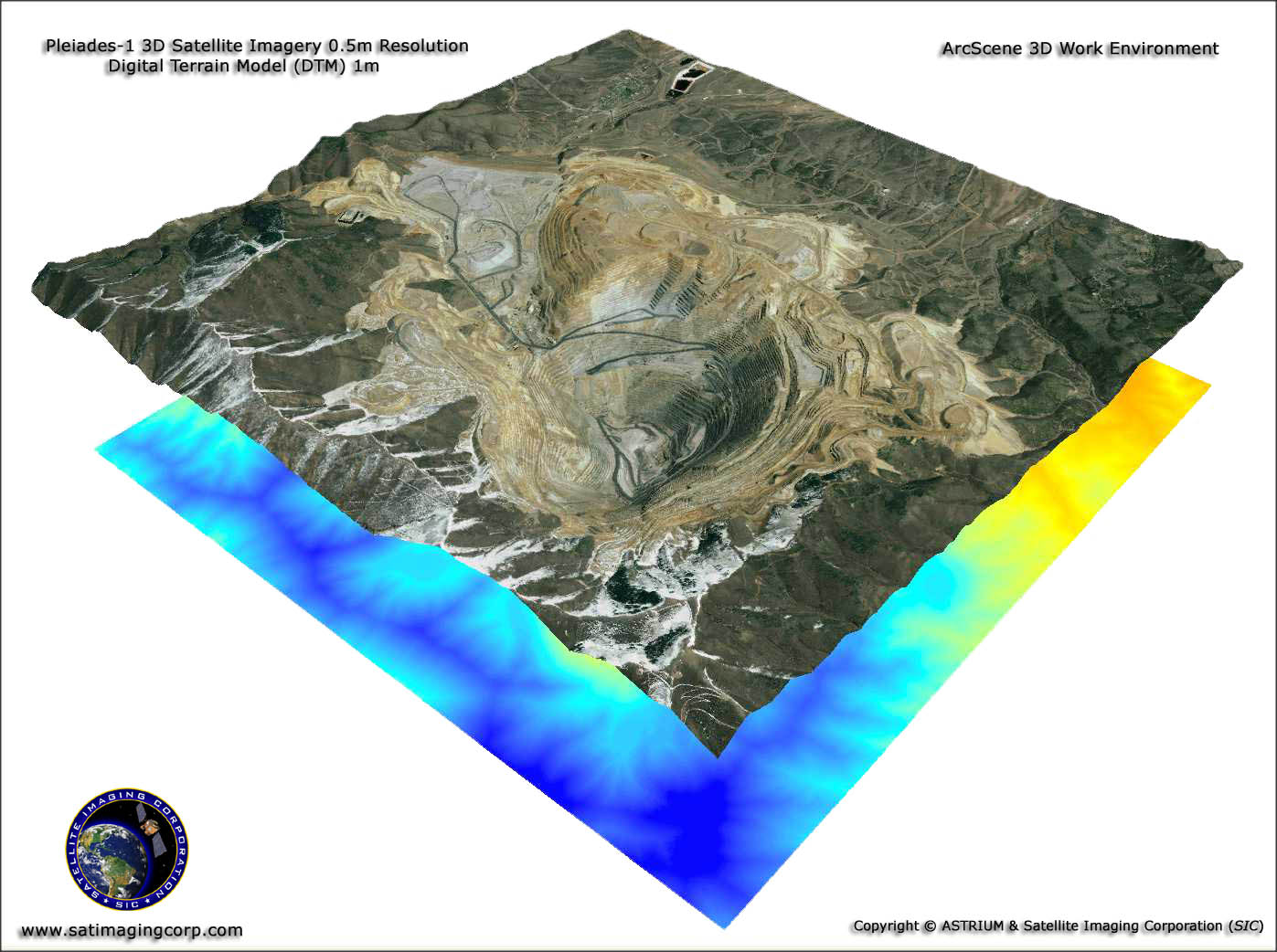
3. Satellite Imagery
Satellites help us examine large forests and cities through their clear detailed pictures for land-use studies and urban development tracking. Free satellite data from Landsat and Sentinel-2 becomes accessible for analysis inside GIS systems.
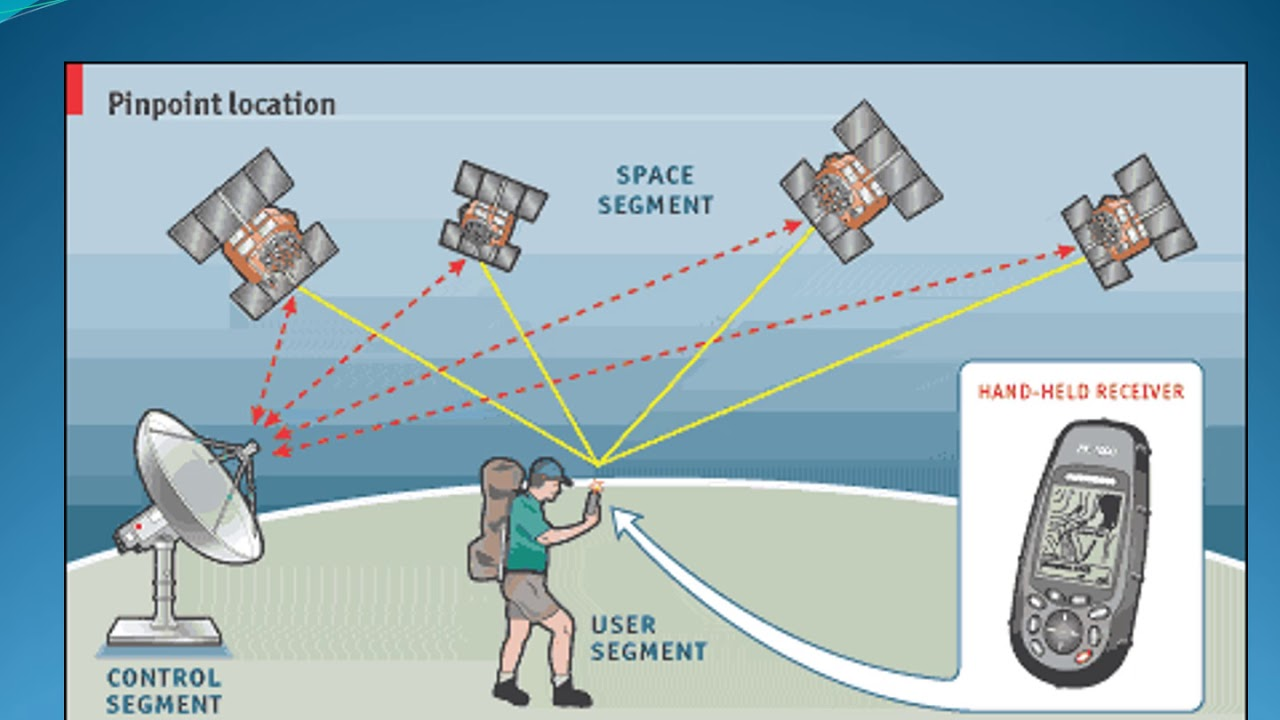
4. GPS (Global Positioning System)
GPS technology and location data help scientists and analysts find exact positions to study wildlife populations and monitor field areas while mapping property boundaries.
5. LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging)
The laser pulses from LiDAR technology build complete 3D maps of land areas and plant life. GIS technology integrates best with these applications including forest monitoring and flood risk assessment plus city development plans.
Organizations achieve better results in natural resource protection by combining GIS with these tools and technologies.
6. Visual and Interactive Content with GIS
The incorporation of visuals and interactive elements with GIS used in natural resource management will not only make the content more engaging but also help readers understand complex concocts easily. This can be done through firstly using maps and infographics such as those that represent forest cover changes or water distribution.
Such maps will help in the visual demonstration of the image GIS has on managing natural resources. 3D maps can also aid in in-depth visualization of terrain and urban landscapes. Infographics by highlighting key statistics and processes such as percentages of deforestation using GIS or creating a guide on the implementation of GIS in watershed management.
Secondly, screenshots of the use of GIS such as QGIs can be used to illustrate how it can be used in real world scenarios.
Moving on, embedded interactive maps from GIS such as from Google Earth engine and simulation videos can also be used, such as GIS simulations of flood modelling.
Lastly, before and after comparisons or images before and after GIS based interventions such as land use changes along with adding links to GIS tutorials will make it easy for users to apply GIS.Such incorporation of visuals and interactive elements will make the content more engaging and help users understand the transformative impact of GIS.
Need Accurate Mapping & Analysis for Resource Management?
GIS Navigator provides precise mapping and real-time data analysis to support informed decision-making in natural resource management.
📞 Schedule a Call | 📩 Email Us | 💼 Get a Quote Now
Benefits of GIS in Natural Resource Management
✓ Improved Decision Making
Better decision-making happens when we turn data into visual and analytical presentations
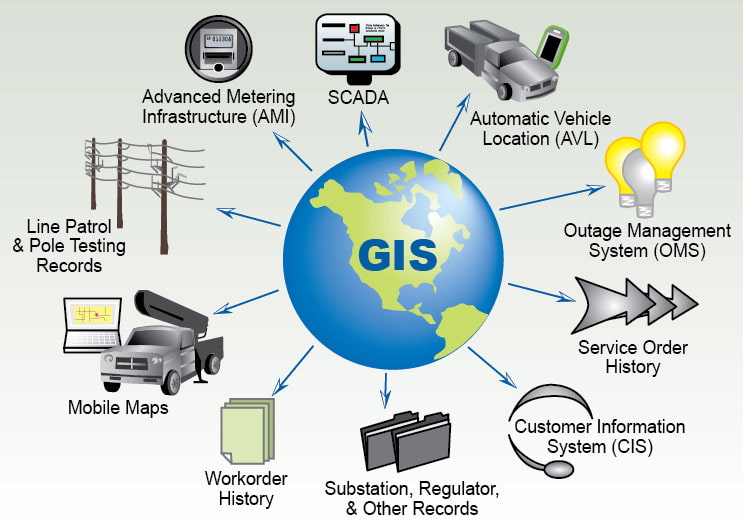
GIS takes raw data and turns it into maps, charts, and dashboards that help people understand difficult information better.
When stakeholders see graphical representations of resources, they can detect hidden patterns in how resources are being used. GIS technology creates maps that show deforestation hotspots and ground water shortage areas so we can take specific action in these areas.
✓ Resource Optimization
GIS helps make better resource placement decisions as its tools help assign resources accurately to their best possible uses. Through geographic information systems managers locate precise spots to put resources to work by planting trees in damaged areas or moving water supplies to regions experiencing shortages. This approach makes better use of resources which decreases unnecessary waste and achieves greater results.
✓ Environmental Protection
Using Geographic Information Systems helps us better monitor and enforce environmental protection actions. GIS serves as a major tool for tracking progress of conservation projects. GIS technology analyzes satellite images to monitor the present state of forests and wildlife while showing how land use patterns develop over time. Organizations use this data to protect wildlife habitats by enforcing rules and stopping crime while tracking the impact of their conservation projects.
✓ Disaster Forecasting and Preparedness
GIS technology helps organizations forecast disasters and make better preparation decisions. Stakeholders use GIS predictive modeling to identify upcoming natural disaster areas and take necessary steps against floods, wildfires, and droughts. GIS technology uses historical and current data to create possible outcomes and locate places most at risk. The early detection system helps organizations prepare better for disasters while protecting both nature and people.
GIS helps organizations save money by making operations smoother and creating better decisions. GIS technology shows us where our resources are located so we don’t waste them.

GIS integration into natural resource management helps us protect the environment more effectively while making our operations better and stronger against climate risks. GIS technology enables us to see and use spatial data effectively to protect our resources while meeting the needs of a growing world.
Challenges and Limitations
Organizations face various obstacles when they use GIS for natural resource management even though this system brings many useful benefits. Below are some key obstacles and limitations:
Data Accessibility and Accuracy: The effectiveness of GIS depends on the availability and reliability of spatial data. In many regions, especially developing areas, access to high-quality data is limited due to inadequate infrastructure or lack of funding. Additionally, outdated or inaccurate data can lead to flawed analyses and poor decision-making. Maintaining up-to-date datasets often requires considerable effort, coordination, and financial resources.
High Costs of Technology and Training: Implementing GIS systems can be expensive, especially for small organizations or projects with limited budgets. The costs include purchasing software and hardware, acquiring high-resolution satellite imagery, and maintaining the necessary infrastructure. Moreover, training staff to use GIS tools and keeping them updated with technological advancements add to the overall expense, making it a barrier for widespread adoption.
GIS tools and analyses require expertise to ensure accurate interpretation and effective application of the data. A shortage of skilled professionals who can manage and analyze GIS data is a significant challenge, particularly in rural or resource-constrained regions. Training existing staff or hiring specialists can be time-consuming and costly, further complicating the integration of GIS into natural resource management workflows.
In many cases, integrating GIS with other technologies or legacy systems poses technical challenges. Compatibility issues can affect data sharing and collaboration across departments or organizations, reducing the efficiency of resource management initiatives.
The use of GIS creates both moral and personal data protection challenges. GIS tracking systems create ethical risks because they monitor personal data that needs protection. To protect personal privacy and maintain ethical standards GIS users must follow legal requirements.
Real-World Examples
GIS has proven transformative in numerous projects worldwide, showcasing its potential in natural resource management:

- State organizations use mapping tools to check drought progress and control groundwater supplies while figuring out better ways to supply water to farms.
- Farmers enhance their production and protect their farmland by using GIS technology to examine soil patterns and track crop health plus estimate future harvests.
- Businesses use GIS data to pick the best areas for wind and solar farms which saves both development expenses and environmental damage.
Transform Your Resource Management Strategies with GIS Navigator!
Leverage geospatial data to optimize resource utilization and promote sustainability.
📞 Schedule a Call | 📩 Email Us | 💼 Get a Quote Now
Conclusion and Future Trends
Advanced technologies help GIS grow stronger in natural resource management. Current GIS technology performs better thanks to machine learning and artificial intelligence which automate data analysis and spot hidden patterns in big data sets.
The connection between IoT devices and GIS systems lets us monitor resource conditions in real time for instance water levels and forest health. Through climate modeling, GIS helps experts forecast environmental shifts and make better policy decisions. By etermining ideal areas for solar and wind farms its role in sustainable development continues to expand.
GIS helps us solve global problems by managing natural resources sustainably and addressing deforestation, water shortage and climate change. Its use in spatial data analysis supports better decision-making while saving resources and is necessary for industries at large. Using GIS programs or backing projects that use this technology helps people and groups move toward better environmental protection.