Mining has always relied on location, precision, and timing. As global demand for critical minerals increases, the margin for error in exploration and planning continues to narrow. Today, the smartest mining decisions aren’t made in the field first, they begin on the map.
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) are reshaping how investors, engineers, and environmental teams plan and manage mining projects. From predicting where to drill to visualising long-term rehabilitation, GIS provides a single spatial framework that guides every decision linked to geography.
At GIS Navigator, we help mining stakeholders use spatial intelligence to reduce uncertainty, improve efficiency, and achieve sustainable growth across projects worldwide.
Looking to make exploration more predictable?
Talk to our GIS team to analyse data faster, find high-value zones, and invest where results matter most.
📞 Schedule a Call | 📩 Email Us | 💼 Get a Quote Now
Why GIS Matters More Than Ever in Mining
Mining companies are under growing pressure to be faster, cleaner, and more transparent. Exploration costs have risen by nearly 12% since 2022, and investors now demand clear environmental proof before backing new projects. At the same time, global ESG frameworks, from the ICMM’s 2025 Responsible Mining Principles to new reporting rules under IFRS S2, require measurable data on land, water, and emissions.

Field surveys alone can’t meet those standards. They take time, cost money, and often leave blind spots. GIS bridges that gap. It connects geological, geochemical, topographic, and environmental layers into one clear picture of the land. What once took months of on-site sampling can now be done in weeks, saving both time and capital.
A 2024 Society for Mining, Metallurgy & Exploration (SME) study found that GIS-based predictive modelling can reduce early-stage fieldwork by up to 40%, helping exploration teams focus only on high-value zones. It doesn’t replace geologists, it makes every survey more targeted and every dollar more effective.
By giving investors real data instead of assumptions, GIS is no longer just a mapping tool. It’s a financial safeguard that helps the industry meet compliance, cut waste, and plan with precision.
GIS in Mineral Exploration: Lowering Investment Risk
Exploration is the most capital-intensive and uncertain part of the mining cycle. Billions are spent each year on drilling that fails to return commercial results. GIS helps reverse that trend by revealing where the odds of success are highest.
a) Integrating Geological, Geophysical, and Geochemical Layers
Each dataset tells only part of the story. Geological maps show rock formations and faults; geophysical data highlights magnetic or gravity changes; geochemical results trace mineral content in soils and streams. GIS brings these pieces together, layering them so patterns become visible. Analysts can test how faults, anomalies, and soil chemistry interact before committing to fieldwork, turning raw data into clear targets.
b) Predictive Mineral-Potential Mapping (ArcGIS, QGIS, MapInfo)
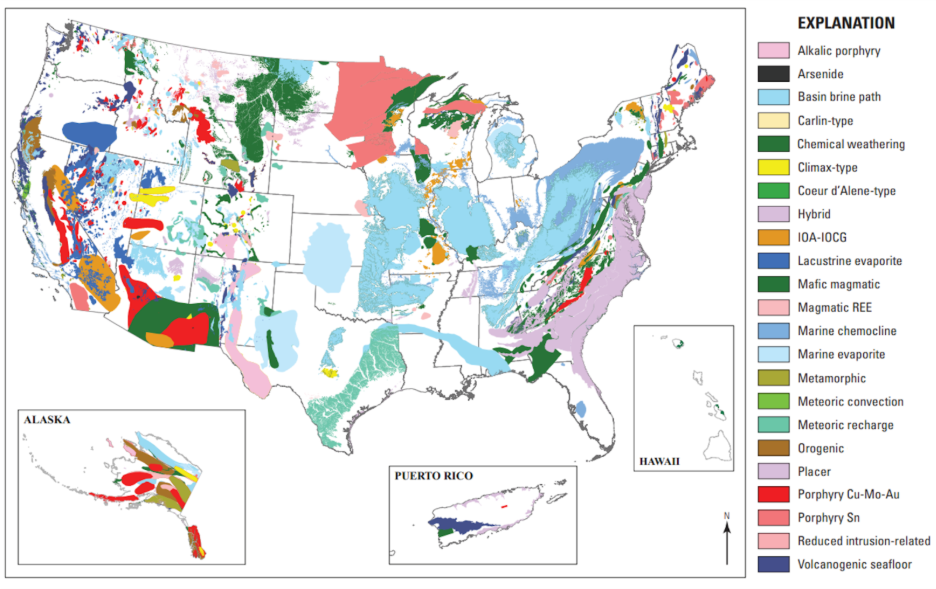
Predictive mapping searches for combinations that match known deposit settings: rock age, structural trend, alteration zone, or metal signature. Using ArcGIS, QGIS, and MapInfo, teams score each location by probability and rank the best prospects. In Cornwall (UK), lithium explorers combine brine chemistry with subsurface geology to pinpoint the most promising zones. Across Ghana, gold exploration firms merge Landsat and Sentinel data to model mineral corridors with minimal on-ground drilling. GIS turns uncertainty into spatial probability and gives investors confidence before funds are deployed.
c) Remote Sensing and Spectral Analysis (Landsat, Sentinel)
Satellite data adds a top-down advantage. Systems like Landsat, Sentinel, and ASTER detect subtle differences in soil tone, vegetation stress, and surface temperature, signals that often mark hydrothermal alteration below. A faint colour shift on a ridge or an area where plants grow poorly can hint at mineral activity. Within GIS, these spectral clues align with field data to create precise exploration zones, reducing random drilling and improving discovery rates.
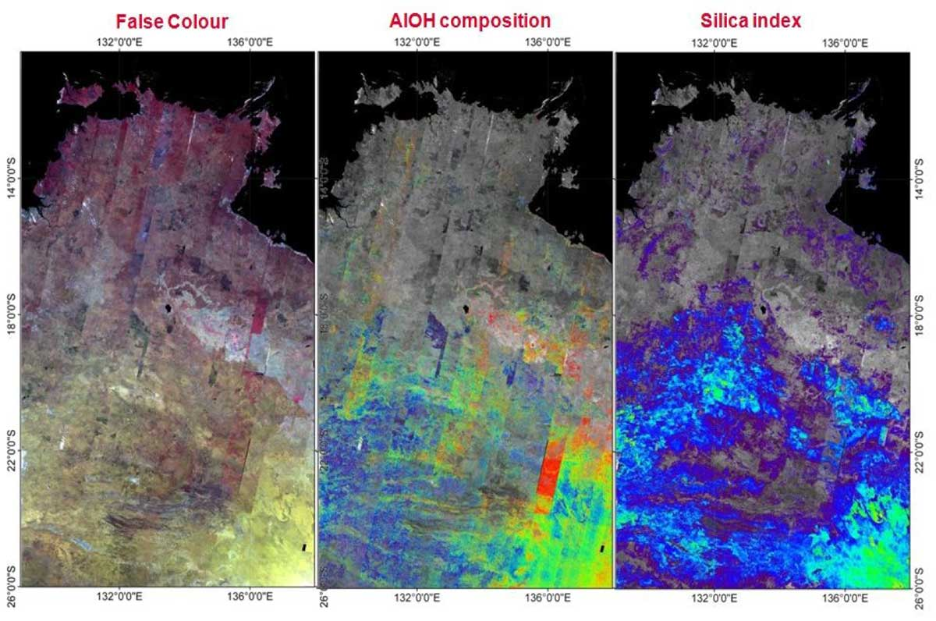

Exploration budgets can run into millions before the first core sample is taken. For investors, that level of uncertainty can make funding early-stage projects a risk rather than an opportunity. GIS changes that by creating an evidence-based roadmap before anyone steps into the field.
By analysing geological, geochemical, and satellite data together, companies can test more sites virtually and discard weaker targets early. This approach shifts spending from speculation to probability. Every dataset reduces risk, and every mapped layer brings capital closer to a confident decision.
Spectral indices such as AlOH and Silica maps help detect alteration halos associated with hydrothermal deposits.
For investors, early GIS adoption directly improves return on investment. Fewer failed drill holes mean less wasted money and a faster route to resource discovery. GIS turns exploration from guesswork into measurable strategy, where budgets stretch further, and success rates rise.
If you want to explore GIS role in mineral exploration in more depth then click here .
GIS for Mine Planning and Design: Turning Data into Structure
Once a viable deposit is confirmed, planning begins, and every decision relies on the land. Engineers must understand terrain, drainage, access, and nearby communities long before excavation starts.
GIS integrates seamlessly with CAD and BIM platforms, allowing planners to visualise 3D terrain, model pit boundaries, and test haul-road designs. Engineers use it to simulate slope stability and manage surface-water flow before breaking ground.
In Saudi Arabia, open-pit phosphate operations use GIS to optimise haul routes, reducing transport fuel use by nearly 15 % while improving safety. Integration of Digital Elevation Models (DEMs) with 3D pit design helps forecast costs and avoid costly re-work. The result: safer mines, better-planned logistics, and stronger compliance documentation.
Post-Mining Rehabilitation: Planning Beyond Extraction
Mining doesn’t end when the last truck leaves the site. The land still has a future, and GIS helps shape it. By analysing digital elevation, soil, and hydrology models, planners design reforestation zones, wetland restoration, and agricultural reuse schemes that match the site’s natural behaviour.
GIS can simulate how rainfall moves across reclaimed land, predicting erosion or waterlogging before they happen. It also helps communities visualise the transformation through easy-to-read maps and 3D renderings.
In South Africa, post-mining landscapes are now modelled in GIS to forecast erosion and guide reforestation corridors, ensuring that rehabilitation plans protect both people and ecosystems. With spatial data leading the way, restoration becomes proactive rather than reactive.
GIS as the Common Language of Mining
Every stakeholder, investor, engineer, regulator, and community group, works with data that lives somewhere on a map. GIS connects these perspectives, creating a shared visual language that aligns financial, technical, and environmental priorities.
Modern systems go further by linking to AI, IoT, and real-time remote sensing, turning GIS into a live decision-intelligence network. Field sensors feed live updates on slope stability or water quality directly into the model, giving decision-makers a dynamic picture instead of a static report.
This unified approach replaces fragmented spreadsheets with one transparent map, where everyone, from exploration analysts to policy-makers, can see progress, risk, and opportunity at the same time.
Ready to see what GIS can do for your next mining project?
Start your project with GIS Navigator to plan every phase, from exploration to rehabilitation, with accuracy and speed.
📞 Schedule a Call | 📩 Email Us | 💼 Get a Quote Now
Conclusion
Mining will always be about extracting value from the ground, but success today depends on how well we understand it. GIS gives mining teams clarity from the first exploration model to the final rehabilitation plan. It helps them act sooner, plan smarter, and build projects that last.
At GIS Navigator, we help mining investors and operators use spatial data to reduce risk, enhance efficiency, and achieve sustainability, from exploration to rehabilitation.
Contact us to explore how GIS can power your next mining project.