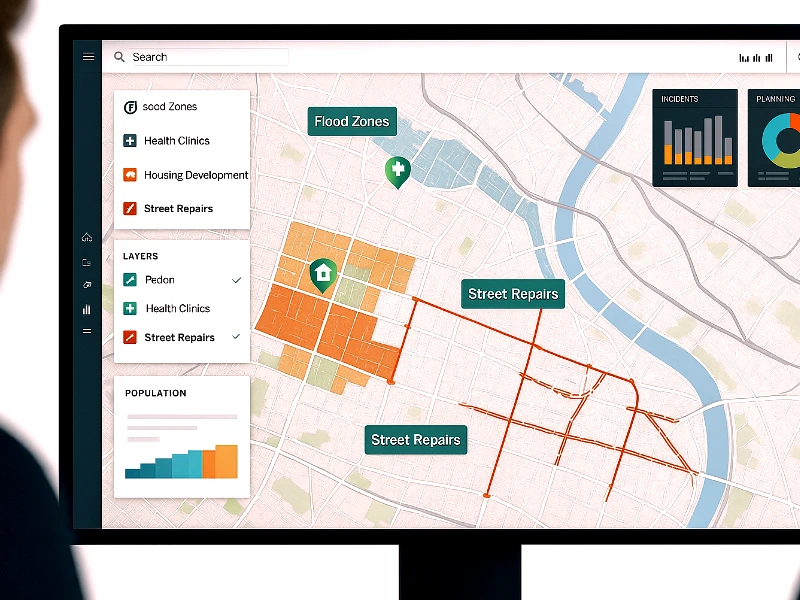
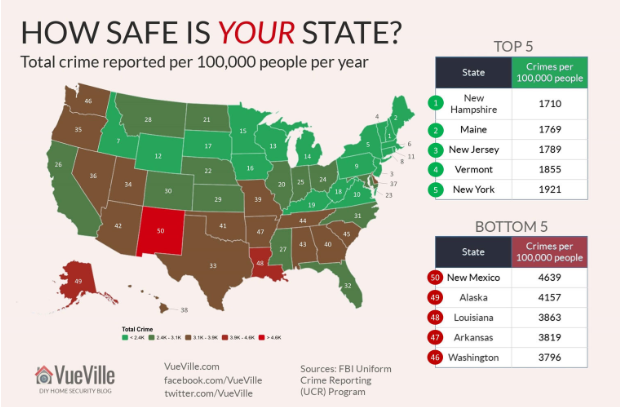
When it comes to building the future better roads, smarter cities and stronger bridges one technology quietly working behind the scenes is GIS, or Geographic Information Systems.
At its core, GIS helps collect, organize, and visualize spatial data that’s the “where” of everything. But in the world of infrastructure and civil engineering, it does so much more. It allows engineers and planners to see patterns, make fast and accurate decisions, and keep projects on track from start to finish.
In this post, we’ll walk through the real-world ways GIS is helping shape infrastructure. We’ll also dive into practical examples showing how it’s not just about maps it’s about smarter planning, reduced risks, and long-term sustainability.
Planning infrastructure without spatial data? That’s like building blind.
Explore how our GIS Planning Services can help you make informed, site-ready decisions from day one.
📞 Schedule a Call | 📩 Email Us | 💼 Get a Quote Now
The Problem
Think of cracked roads, overflowing sewage, or power grids pushed to the limit. Infrastructure faces pressure from every direction aging systems, limited budgets, growing populations. But without accurate, up-to-date information, how do you know what to fix first? Or where to expand?
That’s where GIS makes a difference. It turns confusion into clarity by giving planners the full picture both literally and figuratively.
Why GIS Matters in Infrastructure Planning
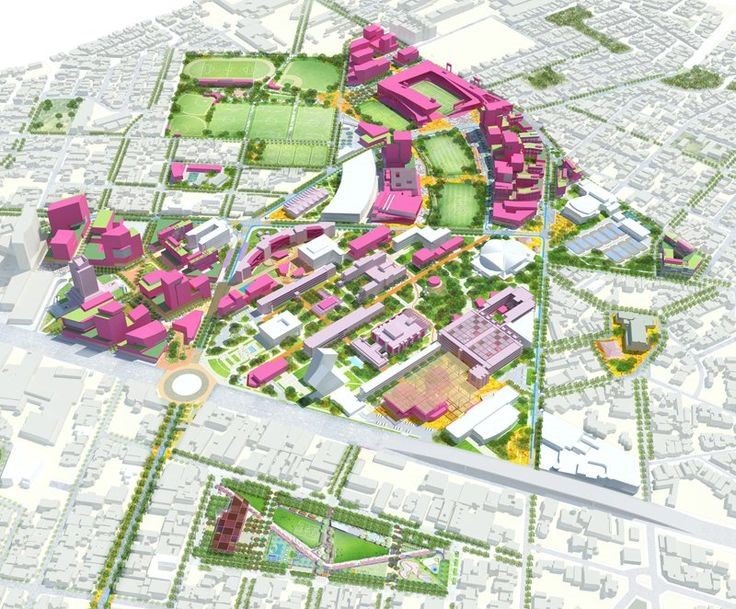
GIS is more than a mapping tool. It’s a smart companion for every stage of infrastructure development.
For example, before breaking ground, planners can use GIS to study the terrain seeing not just hills and valleys but how existing infrastructure, population density, and environmental conditions overlap. That clarity leads to better choices, faster approvals, and safer construction.
It also plays a big role in assessing risks. Flood zones, seismic activity, and soil types GIS puts all this data into one place, helping you avoid costly surprises later.
Need to manage existing infrastructure? GIS keeps tabs on assets like roads, power lines, or water pipes. Want to know when a bridge was last inspected or which section of pipe is likely to fail next? GIS can tell you.
And since budgets are always tight, GIS can help direct resources where they’re needed most based on real data, not just guesswork.
Public engagement? That’s another win. People trust what they can see. By creating easy-to-understand maps and visualizations, GIS helps explain projects to communities, gather feedback, and earn support.
Applications of GIS in Infrastructure
Turning Data Into Visuals
GIS can turn dry spreadsheets into dynamic, interactive maps. These maps can show everything from where sewer lines run to which neighbourhoods are most at risk for traffic jams. This kind of visual clarity helps planners spot issues early and stay ahead of maintenance.
Encouraging Collaboration
GIS is also a collaboration tool. Through mobile apps or web-based platforms, it lets everyone from government agencies to local communities access the same data. That shared understanding builds trust and encourages more inclusive decisions.
Smart Expansion Through Spatial Analysis
Growing a city’s transport system or upgrading power lines? GIS lets planners layer data like population growth, land use, and environmental concerns. With that full view, they can choose locations that serve both present needs and future demands.
Managing Assets Efficiently
From repair logs to inspection reports, GIS stores every detail about infrastructure assets in one place. It helps organizations prioritize what needs fixing, extend the life of valuable assets, and cut down on unnecessary repairs.
From pipes to power lines; know exactly what’s where and what needs attention.
Our asset management services give you complete control over inspections, maintenance logs, and life-cycle planning.
📞 Schedule a Call | 📩 Email Us | 💼 Get a Quote Now
Benefits of Using GIS in Infrastructure Projects
Boosting Efficiency
GIS simplifies time-consuming tasks. For example, instead of sending teams out for early site surveys, planners can use GIS to assess multiple sites remotely. That saves both time and money. Mobile GIS apps also let workers update tasks and access data on the go helping projects stay on track and in sync.
Real-Time Monitoring
Planning is just the beginning. GIS continues to be useful even after the project is built. Sensors installed in roads or bridges can feed data into a GIS system, flagging any wear and tear or structural risks. This early warning system allows for preventative maintenance avoiding expensive emergency repairs down the line.
Comprehensive Analysis
What if you could see how weather, traffic, and population shifts all affect a planned road? With GIS, you can. By combining different kinds of data environmental, structural, social GIS paints a full picture. This helps in smarter design and more resilient infrastructure planning.
Stronger Project Visualizations
GIS is a powerful storytelling tool. Engineers can build 3D models of proposed projects, helping stakeholders and the public understand what’s coming and how it fits in. These visual tools are especially valuable at town halls or planning meetings, where buy-in is key.
Easier Compliance
Infrastructure projects must meet dozens of legal and environmental regulations. GIS helps track these requirements and ensures that designs meet compliance standards. By doing so, it avoids penalties, builds public trust, and paves the way for future approvals.
Case Studies
CPEC: Building a Corridor Across Borders
The China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) is a massive project linking the two countries with roads, pipelines, and railways. Here’s how GIS is playing a key role:
- Mapping the entire corridor with accurate geospatial data
- Choosing optimal routes based on population, terrain, and existing infrastructure
- Assessing environmental impacts like air quality, water use, and land changes
- Optimizing resources including land and utilities
- Supporting real-time surveillance and emergency response
- Helping both countries coordinate the cross-border project efficiently
- Engaging the public by visualizing how the corridor affects communities
- Improving supply chains and logistics for smoother transport
Crossrail (Elizabeth Line), London: A Case from the UK
London’s Crossrail is one of the biggest rail projects in the UK. It connects East and West London through a new high-capacity train line. GIS supported the project at every stage:
- Route planning by layering data on land, population and underground utilities
- Managing land ownership and property acquisitions
- Visualizing complex underground rail systems with 3D models
- Monitoring construction impact on local environments
- Providing real-time updates on train location and passenger data
- Keeping track of train stations, tracks, and maintenance needs
- Involving the public through interactive maps and planning visualizations
Ready to design smarter, safer cities with GIS?
We help engineers and local authorities use geospatial tools to cut costs, reduce risks, and future-proof their infrastructure.
📞 Schedule a Call | 📩 Email Us | 💼 Get a Quote Now
Conclusion
GIS is quietly transforming how we design, build, and maintain infrastructure. By offering a clearer view of the land, helping prevent costly mistakes, and keeping everyone from engineers to everyday citizens informed, GIS has become essential to modern infrastructure.
Looking ahead, as our cities grow and our infrastructure ages, GIS will be even more critical. It’s not just about maps anymore. It’s about building smarter, safer, and more sustainable communities for the next generation.
At GIS Navigator, a top GIS service provider firm, we support infrastructure professionals with location-based tools that simplify planning, asset management, and real-time decision-making. Contact us and see how we can support your next project.