A Geographic Information System, shortly known as GIS, is a framework that is leveraged to capture, store, analyse and visualize spatial or geographic data. The system enables users in various contexts by layering multiple types of data. When the raw data is converted into actionable insights, professionals can not only understand the spatial relationships and patterns but also improve decision-making across several industries.
GIS is particularly essential in telecommunications, especially in the context of deploying and managing Fibre-to-the-Home or FTTH networks. FFTH networks are those networks that offer users high-speed internet that is sent directly to their homes.
The deployment and management of FFTH networks require precise and accurate planning to efficiently enable users to keep using the internet. We must also mention that these processes are comparatively expensive as fiber is deployed for the uninterrupted connectivity of the internet.
Along with that, several other issues can arise while managing logistics, etc. However, by utilizing GIS, professionals such as telecom providers can easily map out the existing infrastructure and thoroughly assess the reach of potential customers while also being able to plan optimal fiber routes without any difficulty.
Allow us to also mention that the use of GIS in managing FFTH networks enables professionals to quickly identify issues and work towards their effective resolution. The response time can also be improved through the visualization of real-time data as well as remote troubleshooting.
GIS is a crucial tool when it comes to telecom companies, especially considering the high-speed internet usage. GIS has become a preferred choice for building sustainable and cost-effective fiber networks across the globe.
Looking for Smarter Telecom Network Planning?
Use our GIS services to map infrastructure, optimize routes, and enhance service coverage.
📞 Schedule a Call | 📩 Email Us | 💼 Get a Quote Now
Importance of FTTH Networks
Since many companies in the world are shifting to the Work-from-Home (WFH) model, a surge can be seen in the context of using high-speed internet. In addition to that, educational institutions depend heavily on high-speed internet to impart online education to their students around the globe or even locally.
Considering all the needs & demands of using the internet at a comparatively higher speed as compared to other industries, we notice a rapid expansion of the Fiber-to-the-Home (FFTH) networks. These networks are deployed to not only deliver faster internet to the users directly to their homes, but they are much more reliable than other sources of the internet.
Many countries specifically include FFTH networks when developing digital infrastructures for the masses. Through this strategic development, those countries will be able to improve internet connectivity and also strengthen economic growth.
We must include that healthy competition can be observed among the telecom providers which enables them to expand FFTH networks at a much higher speed. It is safe to say that expanding such networks has now become a priority, especially in the urban areas. However, telecom providers are working day and night to bridge communication gaps in rural areas as well.
Professionals consider Geographic Information Systems (GIS) a crucial tool to fight challenges that may arise during the deployment of FTTH networks. GIS allows for streamlined route planning while also enabling professionals to carefully analyze spatial data.
This also helps in mapping highly optimal pathways by thoroughly monitoring the related geographic and demographic factors. Leveraging GIS allows for keeping the project costs on the lower side and empowers the stakeholders to make sure that they are efficiently managing the existing assets while quickly identifying if there are areas that might have a higher demand for the internet.
Having access to such details enables stakeholders such as telecom providers to make data-driven decisions, including enhancing network performance.
Moreover, telecom providers can also make the deployment and management processes highly cost-effective. For telecom providers, it’s absolutely necessary to provide the customers with what they are asking for. When the stakeholders efficiently work to fulfil the needs of their customers, they build a strong, customer-centric network. This allows for improving service quality and also helps telecom providers stay ahead in the game.
Read More: Industries that Use GIS
1. Role of GIS in FTTH Network Planning and Design
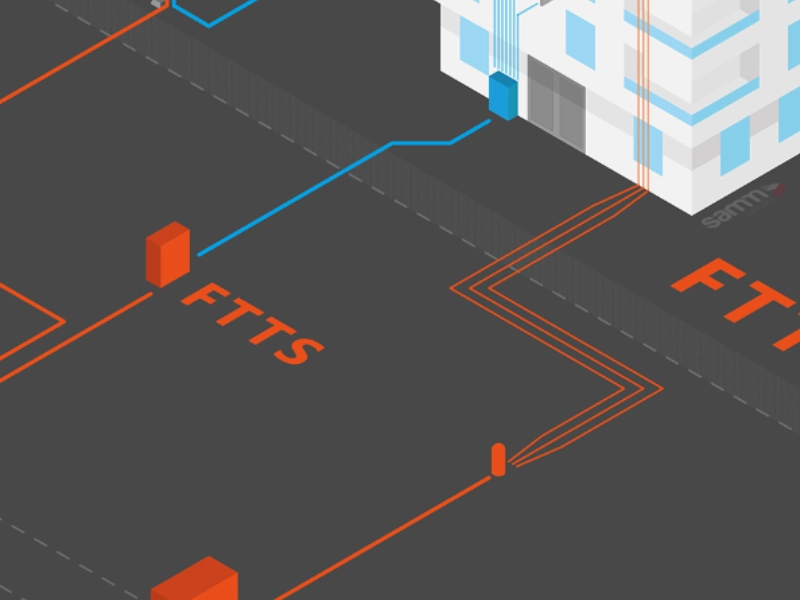
Route Selection for Fibre Deployment
There is no doubt about the fact that GIS has become an essential tool to optimize routes when it comes to laying fibre optic cables effectively. Professionals are in a better position to carefully analyse the geographic and demographic data and then move towards the next steps such as mapping the terrain while also considering the population density.
In addition, professionals can also analyse the existing infrastructure by leveraging GIS and then determine the most optimal pathways to deploy the fibre cables.
Some of the advantages of utilizing GIS for telecommunication utilities are that it helps in the careful identification of the areas with high demands while also enabling the professionals to avoid overlaps with the existing networks in the infrastructures.
We must add that this also allows for enhancing both the speed and accuracy of the planning and deployment processes. GIS is a great tool that empowers telecom companies and network planners by offering them the opportunity to visualize the region in its entirety and also predict the outcomes of a certain project. By having access to detailed and highly accurate data, the teams concerned are in a better position to adapt to changes while also ensuring smooth internet delivery to the customers.
What we like the most about leveraging GIS in any project is that it also allows the stakeholders to assess the environmental factors. So, while the network providers are working on cost-effective solutions for their customers, they can also ensure that their projects won’t cause any harm to the environment.
Let us further explain it in this part of the blog!
When GIS is utilized to develop, deploy and manage networks, professionals can also analyse various factors to reduce disruptions in the natural ecosystems. For example, telecom providers can observe water bodies, protected areas and more to ensure that their projects are highly safe for the environment. This also allows for minimizing the ecological impact wherever possible. Since we all know that ‘sustainability’ is not a buzzword anymore, the stakeholders need to develop highly sustainable networks.
Site Selection for Network Components
Telecom companies also find GIS a powerful tool when it comes to optimal site selection. By offering many different layers of data, GIS enables the stakeholders to identify locations to install poles, cell towers, etc. All of this becomes possible when the concerned teams have access to data such as terrain, population distribution as well as how the users are or will be using the internet.
Through GIS, telecom companies can easily evaluate various factors before they begin the deployment of the networks such as analysing elevation, monitoring proximity to the areas that are populated and also working on the accessibility factor. This data enables the stakeholders to not only meet the technical requirements of a project but also fulfil the needs and demands of the end-users.
Here, we would also like to add that GIS is considered a useful tool to ensure that there is reduced or no interference in the signal strength. This is highly crucial for both fiber optic and wireless communications – regardless of the areas they are deployed.
Stakeholders can easily assess what might be the reasons that are interfering with the signal strength and then work towards making the networks free from all such challenges. This also allows the stakeholders to ensure that they are providing strong signals across all the determined coverage areas.
Would you like to know what is even more interesting in this very context? Well, the use of GIS in site selection enables the stakeholders to minimize all sorts of maintenance costs while also empowering them to provide their customers with high-speed internet that is not only uninterrupted but also highly reliable.
2. Infrastructure Management Using GIS
Asset Management and Tracking
GIS is also a great tool to map and monitor the physical components in fiber optic networks. Those components can be cables, optical splices as well as distribution points. The visualization of such assets enables the stakeholders to always accurately overview the network infrastructures.
The best part is that the required information is available through interactive maps which makes it even easier to know and monitor what is happening.
Through such detailed mapping, telecom operators cannot only track the location and status of the network elements but can also monitor the conditions and see if anything needs to be done to improve the quality of the internet.
GIS happens to be an excellent tool for carrying out efficient asset management which also enables careful and sustainable network expansion as and when required.
One of the most crucial aspects of providing high-speed internet to the end users is to ensure that the networks are being carefully monitored and leveraging GIS facilitates this process by offering real-time updates to the stakeholders.
In addition to that, GIS also provides the concerned teams with data that allows for predictive maintenance. The use of GIS in asset management and tracking enables the stakeholders to ensure that they are offering nothing but high service standards to their customers.
Read More: GIS Services in the Utilities Sector
Operational Efficiency and Maintenance
By leveraging GIS, telecom providers gather real-time situational awareness that not only helps in visualizing the network conditions but also helps in the identification of areas that might need maintenance.
One of the benefits of integrating GIS into telecommunications is that it allows for efficient monitoring of the networks without having to physically inspect the locations. As a result, the stakeholders can also minimize operational costs. GIS empowers professionals in various ways.
For example, in the case of improving the operational efficiency of telecommunication networks, GIS allows for quicker response times to any issue that is present in the systems. This helps in significantly boosting the network’s performance.
Telecommunications is one of the industries that has to have strong relationships with their customers. That can only happen when the stakeholders are eager to stay one step ahead and take care of the whole thing without any major disruptions.
By now, you would know how stakeholders can do so but allow us to say this out loud GIS, when integrated with the operational and business support systems (OSS/BSS) allows for streamlining the workflows. This results in building a strong relationship with the customers. By integrating GIS into the systems, the stakeholders can easily monitor a couple of processes like resource allocation, fault management, etc.
In addition to that, they can also proactively cater to any issues that arise, making sure that their customers are fully satisfied with the services they are paying for.
Need Accurate Utility Mapping & Asset Management?
GIS Navigator helps telecom and utility providers track assets, prevent outages, and improve network efficiency.
📞 Schedule a Call | 📩 Email Us | 💼 Get a Quote Now
3. Customer Service and Network Expansion
Service Availability and Expansion Planning
GIS allows for the strategic expansion of the Fibre-to-the-Home (FTTH) services by helping them visualize areas with high demand. All of this becomes possible when the telecom providers can analyse the demographic trends while also assessing the existing infrastructure.
The data provided by GIS is highly detailed and accurate, allowing the stakeholders to prioritize expansion planning. So, when locations with potential are identified, the concerned teams start working towards making efforts to provide service to areas that are underserved.
GIS does not only serve the telecom providers, in fact, customers can also check service availability through GIS-powered maps in real time. This boosts engagement and also increases the levels of satisfaction among the end users.
GIS helps telecom providers stay highly transparent with their customers as they have access to detailed information regarding service options in the areas they are using the services. It is safe to say that GIS is an invaluable tool to improve customer experience.
Optimizing Network Performance
User needs will continue to evolve in times to come, which means that the telecom providers must be prepared in every sense of the word when it comes to network expansion. In addition to that, they must be able to locate the areas with high demand so that they can fulfil the needs of their customers.
GIS enables the stakeholders to do just that much more efficiently by offering a proactive approach. By carefully analysing the current situation, telecom providers can make informed decisions while also ensuring that all their decisions support the sustainable growth of their projects.
Allow us to also mention that GIS provides stakeholders with real-time data on network performance, enabling them to identify issues in the systems and resolve them before they cause any service disruptions. In short, GIS helps make networks more reliable by enabling the stakeholders to provide consistent service to the end users.
4. Benefits of GIS for Telecommunications Utilities
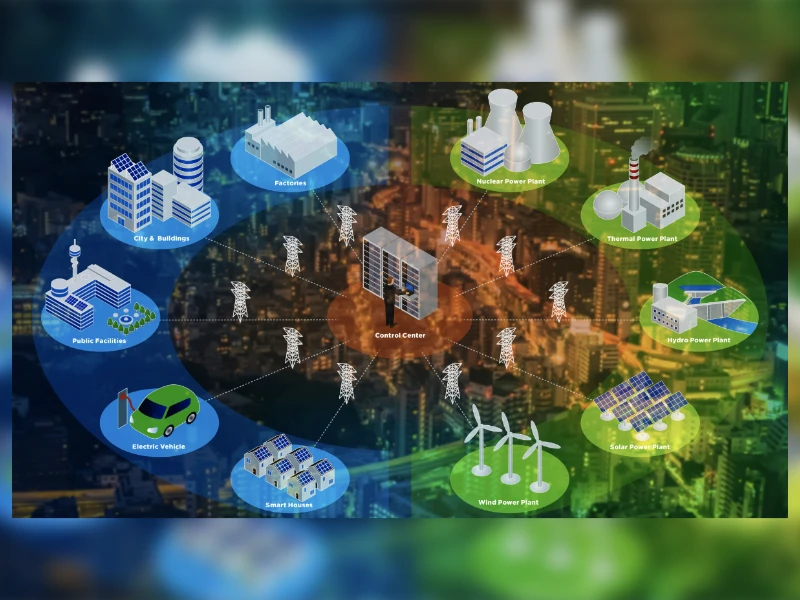

Improved Decision-Making and Cost Savings
By leveraging GIS into their systems, telecom providers are enabled to make data-driven decisions; decisions that help improve network performance, decisions that help visualize planning needs and also identify potential risk areas.
One of the advantages of utilizing GIS is to experience how it transforms raw complex data into easy-to-access, actionable insights. GIS allows the stakeholders to quickly assess the networks and respond to the demands of the customers.
This improves the process of resource allocation ensuring that the investments are utilized where they are needed the most. Moreover, GIS helps in keeping the operational costs on the lower end.
Read More: Benefits of Spatial Data Infrastructure
Enhanced Collaboration and Stakeholder Engagement
GIS is considered an excellent tool to improve coordination and collaboration among stakeholders. This becomes possible when GIS allows the stakeholders to use a centralized platform to perform the required actions.
The up-to-date, shared view of the fiber optic network enables teams from multiple disciplines to make data-driven decisions. Some of the decisions include planning the network expansion to effective deployment.
By leveraging GIS into the telecommunication networks, the stakeholders can experience efficient project management while also avoiding miscommunication among various teams.
GIS Navigator also provides services in the below industry.
Data Integration
In telecommunication utilities, GIS serves as a centralized repository for fiber assets which allows for streamlining data integration across the organization. The database not only enables all the teams to access fiber network information from a single source but also allows them to update it as and when required.
This ensures that the system data is coming from one source and is highly detailed and accurate at the same time. Informed decision-making is crucial for managing telecommunication utilities and GIS allows that to happen at every step of the way.
5. How GIS Navigator Assists in FTTH Network Planning and Management
Customized GIS Solutions for Telecom
GIS Navigator provides customized GIS solutions for telecom utilities, enabling precise network planning and route optimization for FTTH projects.
Infrastructure Management Tools
GIS Navigator offers tools for detailed mapping, tracking, and managing fiber optic infrastructure, ensuring that service providers can efficiently manage assets and minimize downtime.
Read More: Implementation of GIS
Environmental Impact Analysis
GIS Navigator’s services include environmental impact assessments that ensure fiber networks are deployed with minimal environmental disruption, supporting sustainable practices in telecommunications. a reliable and consistent source.
This centralized repository makes it easier to track and manage all assets, streamlining operations and reducing the risk of errors due to inconsistent or outdated information. Data integration using GIS fosters better communication between different teams, allowing them to work collaboratively and efficiently on network projects, from planning to implementation.
Strengthen Your Telecom & Utility Operations with GIS Navigator!
Gain clarity, accuracy, and control with precise geospatial data and analytics.
📞 Schedule a Call | 📩 Email Us | 💼 Get a Quote Now
Conclusion
In conclusion, GIS has proven to be an invaluable tool in the telecommunications industry, especially for the deployment and management of Fiber-to-the-Home (FTTH) networks. By offering spatial insights, GIS optimizes network planning, enhances asset management, and ensures efficient service delivery.
It provides telecom providers with a cost-effective and environmentally conscious way to build robust, high-speed internet networks. As user demands for faster, more reliable internet connections continue to grow, GIS will remain a critical technology for developing and sustaining cutting-edge telecommunications infrastructure, facilitating better collaboration, improving decision-making, and driving customer satisfaction.